Product Description
| Product Information | |
| Product name | Vacuum Pump |
| OEM | 06H145100 F |
| Warranty | 1 year |
| Certifications | CE |
| Condition | Brand-new |
| Appliction | For Audi A3 A4 A5 VW Golf Passat 1.8 2.0 TFSI |
| Brand Name | ZOOMKEY |
| Place of Origin | ZheJiang , China |
| Quality | High-performance |
| Related Products |
| Company Profile |
| Our advantages |
One-stop solution for auto parts
ODM and OEM customized
with 12 months-24 months warranty
high quality, professional service
Zoomrich is a company specialized in distribution and service for CZPT car parts,Especially in Volkswagen, Audi, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Por sche,Jaguar,Land-Rover autoparts.Our business includes temperature control system,suspension parts, engine parts, electrical parts, and some other product lines.We are based in ZheJiang , and cooperate with many international first-line brands in order to meet the customer’s choice of diversity. Based on 12 years of experience,We accumulated a lot of factory resources and build a long-term cooperation in China which include OEM factory,OES resources,IAM factory verified by International famous brand.
About Us
CZPT electronic commerce(ZheJiang )Co.Ltd.is specialized in serving the German car system. The products are suitable for Mercedes-Benz, BMW,Volkswagen imported and other luxury cars. It covers auto engine system, auto transmission system, auto covering system, auto temperature control system,auto suspension and steering system, auto electronic system and so on.
With years of experience in the market of China in auto parts field ,our products have been exported to all over the world simultaneously.We have integrate the R&D,manufacture and trade. Supportina ODM
&OEM customized,and strict support confidentiality of customer brands and property rights. We will try our best to cooperation with you to establish a CZPT relationship.
| AFQ |
1. who are we?
We are based in ZheJiang , China, start from 2017,sell to Western Europe(20.00%),Domestic Market(20.00%),North America(10.00%),South America(10.00%),Eastern Europe(10.00%),Northern Europe(10.00%),Southeast Asia(5.00%),Africa(5.00%),Mid East(5.00%),Eastern Asia(5.00%). There are total about 11-50 people in our office.
2. how can we guarantee quality?
Always a pre-production sample before mass production;
Always final Inspection before shipment;
3.what can you buy from us?
camshaft adjuster,headlamp accessories,cylinder head cover,shock absorber,tensioner
4. why should you buy from us not from other suppliers?
One-stop solution for auto parts ODM and OEM customized with 12 months-24 months warranty
5. what services can we provide?
Accepted Delivery Terms: FOB,CFR,CIF,EXW,Express Delivery;
Accepted Payment Currency:USD,EUR,CNY;
Accepted Payment Type: T/T,L/C,D/P D/A,MoneyGram,PayPal,Western Union,Cash;
Language Spoken:English,Chinese
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Product Name: | Vacuum Pump |
| Certificates: | CE RoHS Ts16949 |
| Package: | Carton Box |
| Quality: | High-Performance |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
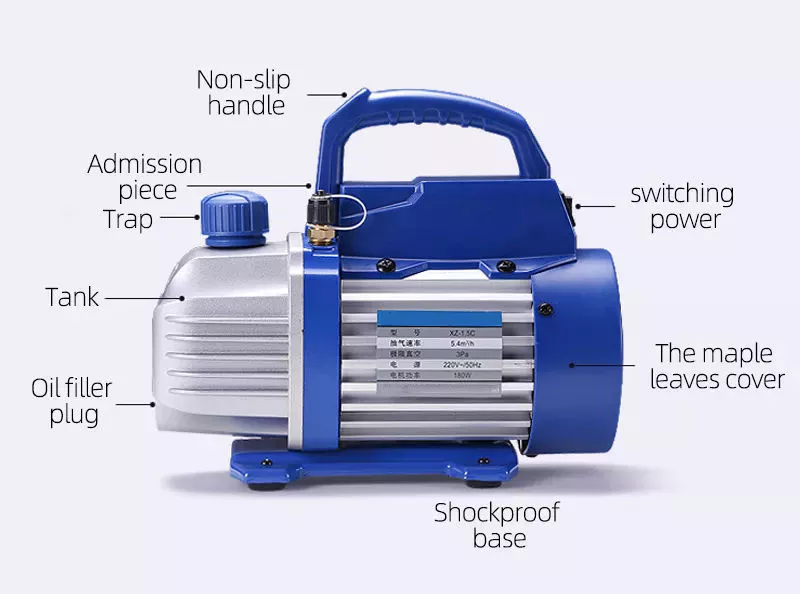
How to install a vacuum pump
A vacuum pump creates a relative vacuum within a sealed volume by drawing gas molecules from the sealed volume. Vacuum pumps can be used in a variety of industrial applications. They also offer various lubrication options. If you are considering purchasing, please understand its functions and features before purchasing.
How it works
The working principle of a vacuum pump is called gas transfer. The principle can be further divided into two basic categories: positive displacement and momentum transfer. At high pressure and moderate vacuum, gas molecules collide and move and create a viscous flow. At higher vacuum levels, gas molecules separate to create molecular or transitional flows.
Another principle of vacuum pumps is fluid-tightness. There are two main types of seals: rotary seals and screw seals. Rotary seals prevent liquid leakage, while screw seals only allow liquids to flow out at higher pressures. Some pumps may not use the third seal.
The flow rate of the vacuum pump determines the machine’s ability to pump a certain amount of material. A higher pumping speed will shorten the drain time. Therefore, the mass flow of the vacuum pump must be carefully considered. The speed and type of vacuum must also be considered.
The working principle of a vacuum pump is to push gas molecules from a high-pressure state to a low-pressure state. This creates a partial vacuum. There are many different types of vacuum pumps, each with different functions. Some are mechanical, some are chemical. In either case, their function is the same: to create a partial or complete vacuum. Vacuum pumps use a variety of technologies and are sized according to the application. Proper sizing is critical for optimum efficiency.
Gas transfer pumps use the same principles as vacuum pumps but use different technology. One of the earliest examples is the Archimedes spiral. Its structure consists of a single screw inside a hollow cylinder. More modern designs use double or triple screws. The rotation of the screw causes gas molecules to be trapped in the cavity between the screw and the housing. The fluid is then discharged at slightly above atmospheric pressure. This difference is called the compression ratio.
Another type of vacuum pump is a diffusion pump. Its main use is industrial vacuum processing. It is used in applications such as mass spectrometry, nanotechnology and analytical instrumentation. These pumps are generally inexpensive to purchase and operate.
Apply
Vacuum pumps are essential for many scientific and industrial processes. They are used in the production of vacuum tubes, CRTs, lamps and semiconductor processing. They can also be used to support mechanical equipment. For example, they can be mounted on the engine of a motor vehicle. Likewise, they can be used to power hydraulic components of aircraft. Among other uses, the vacuum pump helps calibrate the gyroscope.
Vacuum pumps are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry and are one of the largest users of this technology. They help deal with hazardous materials and eliminate waste quickly. They are also used in power jets, dump fuel tanks and rear doors, among others. However, they are sensitive to contamination and should only be used in environments where leaks can be prevented. Therefore, choosing the right fluid for the application is very important.
The most popular type of vacuum pump is the rotary vane pump. These pumps are known for their high pumping speed and low pressure. Their efficient pumping capacity allows them to reach pressures below 10-6 bar. Additionally, they are usually oil-sealed and have excellent vacuuming capabilities.
Vacuum pumps are often used to remove air from closed systems. They create a vacuum by reducing the density of the air in the compressed space. This is done by using the mechanical force energy generated by the rotating shaft. When the pump is under pressure, it converts this energy into pneumatic power. When the pressure is different, the energy produced depends on the volume of the gas and the pressure difference between the inner and outer atmospheres.
Vacuum pumps are also used in the manufacture of solar cells. They are used in the manufacture of solar cells, including ingot casting processes as well as cell and module processes. The design of the vacuum system plays an important role in reducing the cost of the process, thus making it profitable. Due to their low maintenance costs, they are an invaluable tool for making solar cells.
Vacuum pumps are widely used in many applications. In addition to industrial and research uses, they are also used in water remediation. 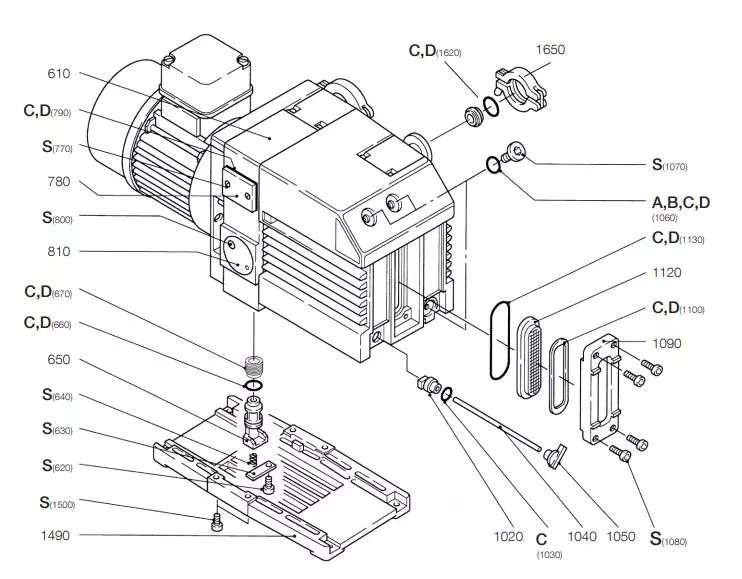
Oil Lubrication Option
Vacuum pumps are available in a variety of oil lubrication options. Choosing the right lubricant can help protect your vacuum pump and maximize its performance. Different base oils may contain different additives, such as antioxidants, and some contain additional additives for specific purposes. You should choose an oil with the right concentration of these additives for optimal lubrication of your vacuum pump.
Vacuum pumps are usually lubricated with paraffinic mineral oil. However, this type of lubricant evaporates as the temperature increases. To minimize evaporative losses, choose a lubricant with low vapor pressure. Also, you should choose lubricants that are resistant to extreme temperatures. Extreme temperatures can put extra stress on the oil and can even significantly shorten the life of the oil.
In terms of viscosity, synthetic oils are the best choice for vacuum pumps. These types of oils are designed to resist gas dissolution and are more resistant to corrosion. Therefore, synthetic oils are ideal for handling aggressive substances. Whether or not your pump needs lubrication, choosing a quality product is important.
The vacuum pump oil should be changed periodically according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. If you use a filter, you should also change the oil as soon as the filter reaches the end of its life. Unplanned oil changes will eventually cause the vacuum pump to not reach its maximum vacuum capacity.
You can buy vacuum pump oil from vacuum pump manufacturers or other suppliers. These options are available in a variety of sizes, and labels can be customized. The oil should be designed for the pump. However, you should check the manufacturer’s recommendations to avoid buying the wrong type.
If you choose to use a synthetic oil, it is important to use a good quality oil. It helps the pump work more efficiently and prolong its life.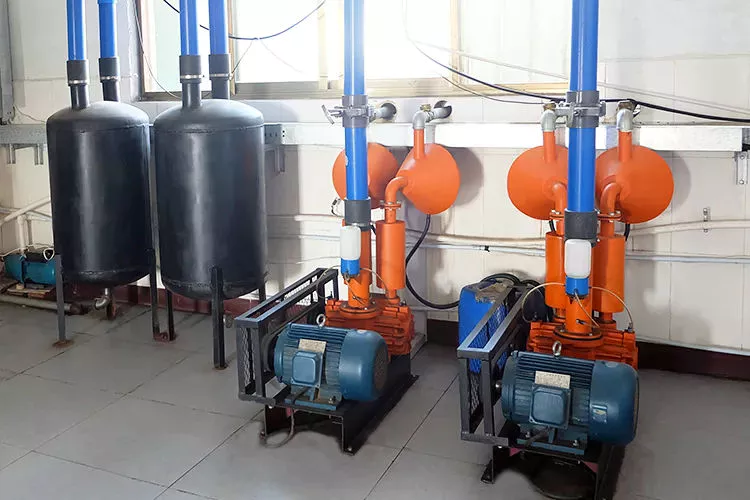 
Install
After choosing a suitable location, the next step is to install the pump. First, place the pump on a flat surface. Then, screw the pump onto the motor body above the check valve. Make sure the accessories are wrapped with sealing tape and secured with screws. The direction of gas inflow and outflow is indicated by arrows on the pump. The direction of rotation around the pump is also shown.
During commissioning, check the operation of each part of the pump. If the pump is equipped with a pipe connection, the pipe should be the same size and shape as the pump flange. Also, make sure that the piping does not cause any pressure drop. In addition, the first three weeks of operation require the installation of protective nets at the suction ports.
When selecting a pump, consider the back pressure of the system. Too much back pressure will affect the capacity of the vacuum pump. Also, check the temperature of the seal. If the temperature is too high, the seal may be damaged. It could also be due to a partially closed valve in the recirculation line or a clogged filter. Circulation pumps and heat exchangers should also be checked for fouling.
The vacuum pump is usually installed in the chassis area of the car. They can be mounted next to the engine or on a lower support frame. They are usually fastened to the bracket using suitable shock absorbers and isolating elements. However, before installing the vacuum pump, be sure to check the vacuum pump’s wiring harness before connecting it to the vehicle.
In many experimental setups, a vacuum pump is essential. However, improperly installed vacuum pumps can expose users to harmful vapors and chemicals. Appropriate plugs and belt guards should be installed to prevent any accidental chemical exposure. It is also important to install a fume hood for the pump.
In most cases, vacuum pumps come with installation manuals and instructions. Some manufacturers even offer start-up assistance if needed.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
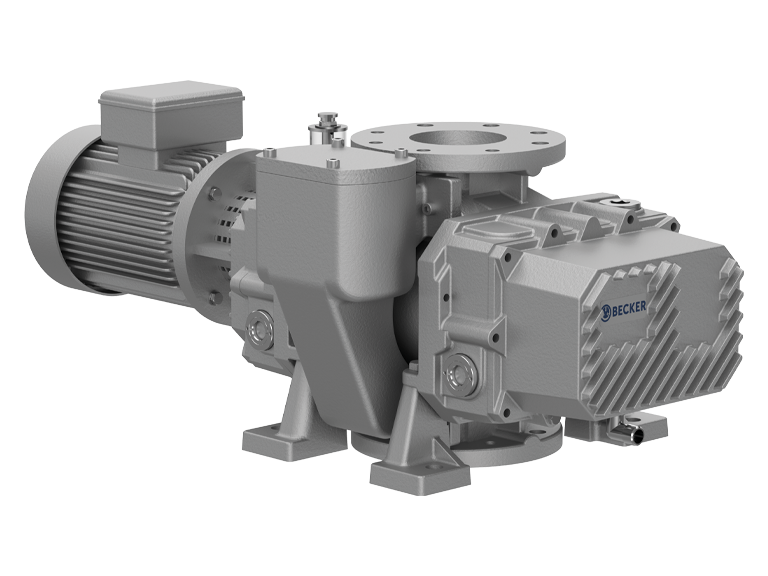
China Professional 20m3/H Air Cooled Screw Vacuum Pump for Biological Medicine Food Chemical with Oilless No Oil and Clean Vacuum vacuum pump engine
Product Description
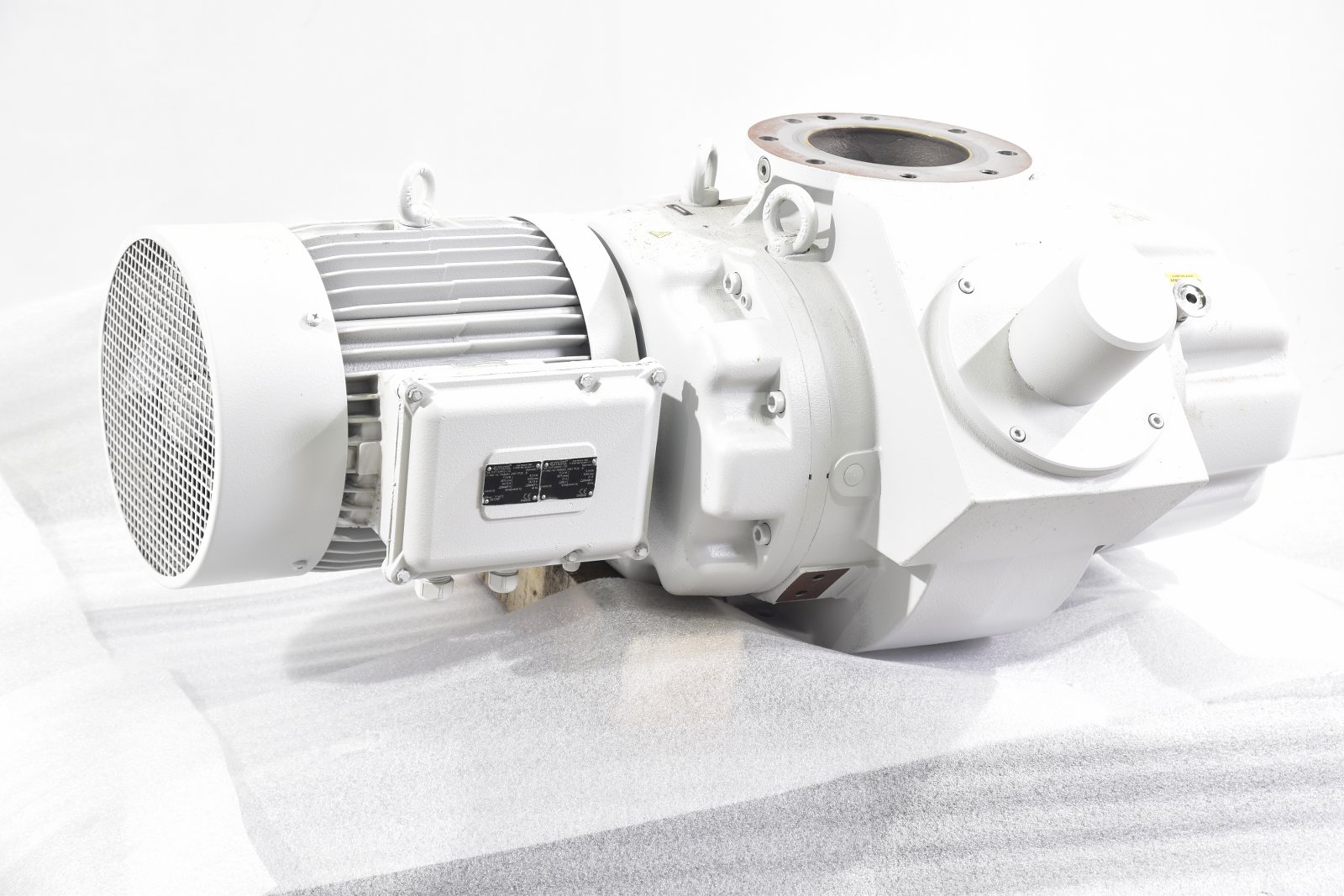
Dry Screw Vacuum Pump RSB571
Product Description
Dry screw vacuum pump, is the use of a pair of screw, made in the pump shell synchronous high-speed reverse rotation of the effects of the suction and exhaust and suction device, 2 screw fine dynamic balancing correction, and is supported by bearings, is installed in the pump shell, between screw and screw has a certain gap, so the pump work, no friction between each other, smooth running, low noise, Working chamber without lubricating oil, therefore, dry screw pump can remove a lot of steam and a small amount of dust gas occasions, higher limit vacuum, lower power consumption, energy saving, maintenance-free and other advantages.
There is no medium in the working chamber, which can obtain a clean vacuum.
No clearance between rotating parts, high speed operation, small overall volume.
There is no compression in the gas, suitable for extraction of coagulable gas.
Can remove a lot of steam and a small amount of dust gas occasions.
High vacuum, the ultimate vacuum up to 1 Pa.
Screw material is high strength special material, material density, wear resistance, stable performance.
No friction rotating parts, low noise.
Simple structure, convenient maintenance.
Wider range of use: corrosive environment can be used.
No oil consumption, no water.
Pump gas directly discharged from the pump body, no pollution of water, no environmental pressure, more convenient gas recovery.
It can be composed of oil-free unit with Roots pump and molecular pump.
Product Parameters
| Product Model | 50/60Hz | RSB571 |
| Pumping Speed | 50Hz | 18m³/H |
| 60Hz | 22m³/H | |
| Ultimate Pressure | mbar | 0.03 |
| Inlet Diameter | KF40 | |
| Voltage | 50Hz | 200-240/345-415V |
| 60Hz | 220-275/380-480V | |
| Motor Power | kW | 1.5 |
| Rotate Speed | r/min | 2900/3500 |
| Noise Level | dB | 72 |
| Cooling Mode | Air Cooling | |
| Net Weight | kg | 48 |
Detailed Photos
Installation Instructions
Certifications
Company Profile
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Screw Number: | Double Screw Pump |
|---|---|
| Screw Suction Method: | Single Suction |
| Pump Shaft Position: | Horizontal |
| Performance: | Anticorrosion |
| Application: | Chemical |
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
| Samples: |
US$ 4500/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Are Vacuum Pumps Employed in the Production of Electronic Components?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the production of electronic components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The production of electronic components often requires controlled environments with low or no atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pumps are employed in various stages of the production process to create and maintain these vacuum conditions. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps are used in the production of electronic components:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in deposition processes, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which are commonly employed for thin film deposition on electronic components. These processes involve the deposition of materials onto substrates in a vacuum chamber. Vacuum pumps help create and maintain the necessary vacuum conditions required for precise and controlled deposition of the thin films.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Etching and cleaning processes are essential in the fabrication of electronic components. Vacuum pumps are used to create a vacuum environment in etching and cleaning chambers, where reactive gases or plasmas are employed to remove unwanted materials or residues from the surfaces of the components. The vacuum pumps help evacuate the chamber and ensure the efficient removal of byproducts and waste gases.
3. Drying and Bake-out: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the drying and bake-out processes of electronic components. After wet processes, such as cleaning or wet etching, components need to be dried thoroughly. Vacuum pumps help create a vacuum environment that facilitates the removal of moisture or solvents from the components, ensuring their dryness before subsequent processing steps. Additionally, vacuum bake-out is employed to remove moisture or other contaminants trapped within the components’ materials or structures, enhancing their reliability and performance.
4. Encapsulation and Packaging: Vacuum pumps are involved in the encapsulation and packaging stages of electronic component production. These processes often require the use of vacuum-sealed packaging to protect the components from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the packaging materials, creating a vacuum-sealed environment that helps maintain the integrity and longevity of the electronic components.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Vacuum pumps are utilized in testing and quality control processes for electronic components. Some types of testing, such as hermeticity testing, require the creation of a vacuum environment for evaluating the sealing integrity of electronic packages. Vacuum pumps help evacuate the testing chambers, ensuring accurate and reliable test results.
6. Soldering and Brazing: Vacuum pumps play a role in soldering and brazing processes for joining electronic components and assemblies. Vacuum soldering is a technique used to achieve high-quality solder joints by removing air and reducing the risk of voids, flux residuals, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the soldering chambers, creating the required vacuum conditions for precise and reliable soldering or brazing.
7. Surface Treatment: Vacuum pumps are employed in surface treatment processes for electronic components. These processes include plasma cleaning, surface activation, or surface modification techniques. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum environment where plasma or reactive gases are used to treat the component surfaces, improving adhesion, promoting bonding, or altering surface properties.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may be used in electronic component production, depending on the specific process requirements. Commonly used vacuum pump technologies include rotary vane pumps, turbo pumps, cryogenic pumps, and dry pumps.
In summary, vacuum pumps are essential in the production of electronic components, facilitating deposition processes, etching and cleaning operations, drying and bake-out stages, encapsulation and packaging, testing and quality control, soldering and brazing, as well as surface treatment. They enable the creation and maintenance of controlled vacuum environments, ensuring precise and reliable manufacturing processes for electronic components.
What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to support a range of critical operations. Some of the key roles of vacuum pumps in pharmaceutical manufacturing include:
1. Drying and Evaporation: Vacuum pumps are employed in drying and evaporation processes within the pharmaceutical industry. They facilitate the removal of moisture or solvents from pharmaceutical products or intermediates. Vacuum drying chambers or evaporators utilize vacuum pumps to create low-pressure conditions, which lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate at lower temperatures. By applying vacuum, moisture or solvents can be efficiently removed from substances such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), granules, powders, or coatings, ensuring the desired product quality and stability.
2. Filtration and Filtrate Recovery: Vacuum pumps are used in filtration processes for the separation of solid-liquid mixtures. Vacuum filtration systems typically employ a filter medium, such as filter paper or membranes, to retain solids while allowing the liquid portion to pass through. By applying vacuum to the filtration apparatus, the liquid is drawn through the filter medium, leaving behind the solids. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient filtration, speeding up the process and improving product quality. Additionally, vacuum pumps can aid in filtrate recovery by collecting and transferring the filtrate for further processing or reuse.
3. Distillation and Purification: Vacuum pumps are essential in distillation and purification processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Distillation involves the separation of liquid mixtures based on their different boiling points. By creating a vacuum environment, vacuum pumps lower the boiling points of the components, allowing them to vaporize and separate more easily. This enables efficient separation and purification of pharmaceutical compounds, including the removal of impurities or the isolation of specific components. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various distillation setups, such as rotary evaporators or thin film evaporators, to achieve precise control over the distillation conditions.
4. Freeze Drying (Lyophilization): Vacuum pumps are integral to the freeze drying process, also known as lyophilization. Lyophilization is a dehydration technique that involves the removal of water or solvents from pharmaceutical products while preserving their structure and integrity. Vacuum pumps create a low-pressure environment in freeze drying chambers, allowing the frozen product to undergo sublimation. During sublimation, the frozen water or solvent directly transitions from the solid phase to the vapor phase, bypassing the liquid phase. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient and controlled sublimation, leading to the production of stable, shelf-stable pharmaceutical products with extended shelf life.
5. Tablet and Capsule Manufacturing: Vacuum pumps are utilized in tablet and capsule manufacturing processes. They are involved in the creation of vacuum within tablet presses or capsule filling machines. By applying vacuum, the air is removed from the die cavity or capsule cavity, allowing for the precise filling of powders or granules. Vacuum pumps contribute to the production of uniform and well-formed tablets or capsules by ensuring accurate dosing and minimizing air entrapment, which can affect the final product quality.
6. Sterilization and Decontamination: Vacuum pumps are employed in sterilization and decontamination processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Autoclaves and sterilizers utilize vacuum pumps to create a vacuum environment before introducing steam or chemical sterilants. By removing air or gases from the chamber, vacuum pumps assist in achieving effective sterilization or decontamination by enhancing the penetration and distribution of sterilants. Vacuum pumps also aid in the removal of sterilants and residues after the sterilization process is complete.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry screw pumps, or liquid ring pumps, may be utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing depending on the specific requirements of the process and the compatibility with pharmaceutical products.
In summary, vacuum pumps play a vital role in various stages of pharmaceutical manufacturing, including drying and evaporation, filtration and filtrate recovery, distillation and purification, freeze drying (lyophilization), tablet and capsule manufacturing, as well as sterilization and decontamination. By enabling efficient and controlled processes, vacuum pumps contribute to the production of high-quality pharmaceutical products, ensuring the desired characteristics, stability, and safety.

What Are the Primary Applications of Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Industrial Processes:
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in numerous industrial processes, including:
– Vacuum Distillation: Vacuum pumps are used in distillation processes to lower the boiling points of substances, enabling separation and purification of various chemicals and compounds.
– Vacuum Drying: Vacuum pumps aid in drying processes by creating a low-pressure environment, which accelerates moisture removal from materials without excessive heat.
– Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in the food industry to remove air from packaging containers, prolonging the shelf life of perishable goods by reducing oxygen exposure.
– Vacuum Filtration: Filtration processes can benefit from vacuum pumps to enhance filtration rates by applying suction, facilitating faster separation of solids and liquids.
2. Laboratory and Research:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories and research facilities for various applications:
– Vacuum Chambers: Vacuum pumps create controlled low-pressure environments within chambers for conducting experiments, testing materials, or simulating specific conditions.
– Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometers often utilize vacuum pumps to create the necessary vacuum conditions for ionization and analysis of samples.
– Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps enable freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to a vacuum, allowing the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor state.
– Electron Microscopy: Vacuum pumps are essential for electron microscopy techniques, providing the necessary vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging of samples.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics Industries:
High vacuum pumps are critical in the semiconductor and electronics industries for manufacturing and testing processes:
– Semiconductor Fabrication: Vacuum pumps are used in various stages of chip manufacturing, including deposition, etching, and ion implantation processes.
– Thin Film Deposition: Vacuum pumps create the required vacuum conditions for depositing thin films of materials onto substrates, as done in the production of solar panels, optical coatings, and electronic components.
– Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in leak testing applications to detect and locate leaks in electronic components, systems, or pipelines.
4. Medical and Healthcare:
Vacuum pumps have several applications in the medical and healthcare sectors:
– Vacuum Assisted Wound Closure: Vacuum pumps are used in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), where they create a controlled vacuum environment to promote wound healing and removal of excess fluids.
– Laboratory Equipment: Vacuum pumps are essential in medical and scientific equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and centrifugal concentrators.
– Anesthesia and Medical Suction: Vacuum pumps are utilized in anesthesia machines and medical suction devices to create suction and remove fluids or gases from the patient’s body.
5. HVAC and Refrigeration:
Vacuum pumps are employed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries:
– Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Vacuum pumps are used during system installation, maintenance, and repair to evacuate moisture and air from refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring efficient operation.
– Vacuum Insulation Panels: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the manufacturing of vacuum insulation panels, which offer superior insulation properties for buildings and appliances.
6. Power Generation:
Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation applications:
– Steam Condenser Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in power plants to remove non-condensable gases from steam condenser systems, improving thermal efficiency.
– Gas Capture: Vacuum pumps are utilized to capture and remove gases, such as hydrogen or helium, in nuclear power plants, research reactors, or particle accelerators.
These are just a few examples of the primary applications of vacuum pumps. The versatility and wide range of vacuum pump types make them essential in numerous industries, contributing to various manufacturing processes, research endeavors, and technological advancements.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Standard High Efficiency with Electric Vacuum Pump RS-2 vacuum pump
Product Description
| Item | Double Stages rotary vane air Vacuum Pump |
| Voltage | 110V/60HZ 220V/50HZ |
| Free Air Displacement | 12/10 CFM |
| Ultimate Vacuum | 0.3pa |
| Rotating Speed | 1720/1440 |
| Power(HP) | 1 |
| Oil Capacity(ml) | 500 |
| Dimension(mm) | 430X142X280 |
| Weight(kg) | 17 |
| Pcakage | One or 2 sets packed in a Canton |
| Payment Terms | T/T L/C West Union |
| Certificate | CE |
HangZhou CHINAMFG Refrigeration Technology Co., Ltd. is a large modern chemical enterprise specializing in manufacturing, researching and exporting high purity fluoro-chemicals, fine chemicals, hydrocarbon chemicals, etc. Its headquarter locates in ZheJiang capital HangZhou city, and has 2 profound manufacturing bases, separately in HangZhou City of ZheJiang Province and HangZhou city of ZHangZhoug Province. Our company takes “Science and Technology, Environmental Protection, Internationalization” as development direction and “First-class Technology, First-class Quality, First-class Service, First-class Efficiency” as service tenet.
Main Products:
R22 , R134A , R410A , R407c , R507 , R404A , R600 Refrigerant Gas, Manifold Gauge ,vacuum pump, compressor,etc.
Customer’s satisfactory is our forever pursue
FAQ:
Q: If there’s space for you to lower the price?
A: The price in that field is changeable, so, fell free to ask for latest price and I’ll provide you the lowest.
Q: Could I use my own LOGO or design on goods?
A: Customized logo and design on mass production are available.
Q: Can I visit your factory?
A: Sure, welcome any time. We can also pick you up at air port and station.
Q: What is the delivery time?
A: One week for sample, 15 to 20 days for mass production.
Q: How about the payment term?
A: TT,L/C at sight, Paypal,Western Union, etc. Normally 30% T/T in advance, 30% TT before shipment, the balance against the copy of B/L in 7 days.
Q: How much discount can you offer?
A: We will do our best to offer the competitive price,usually the discount depends on th quantity.
Q:The shipping fare costs too much ,can you make it cheaper for us?
A: We will try our best to negotiate with shipping company,we save every penny for our customers,if it is possible ,you can desinate your own shipping agency.
Q: Can I trust you?
A: Absolutely YES. We are “made in china” verified supplier.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Working Conditions: | Dry |
| Specification: | 7kg |
| Trademark: | Henbin |
| Samples: |
US$ 40/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Are the Advantages of Using Oil-Sealed Vacuum Pumps?
Oil-sealed vacuum pumps offer several advantages in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. High Vacuum Performance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are known for their ability to achieve high levels of vacuum. They can create and maintain deep vacuum levels, making them suitable for applications that require a low-pressure environment. The use of oil as a sealing and lubricating medium helps in achieving efficient vacuum performance.
2. Wide Operating Range: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps have a wide operating range, allowing them to handle a broad spectrum of vacuum levels. They can operate effectively in both low-pressure and high-vacuum conditions, making them versatile for different applications across various industries.
3. Efficient and Reliable Operation: These pumps are known for their reliability and consistent performance. The oil-sealed design provides effective sealing, preventing air leakage and maintaining a stable vacuum level. They are designed to operate continuously for extended periods without significant performance degradation, making them suitable for continuous industrial processes.
4. Contamination Handling: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are effective in handling certain types of contaminants that may be present in the process gases or air being evacuated. The oil acts as a barrier, trapping and absorbing certain particulates, moisture, and chemical vapors, preventing them from reaching the pump mechanism. This helps protect the pump internals from potential damage and contributes to the longevity of the pump.
5. Thermal Stability: The presence of oil in these pumps helps in dissipating heat generated during operation, contributing to their thermal stability. The oil absorbs and carries away heat, preventing excessive temperature rise within the pump. This thermal stability allows for consistent performance even during prolonged operation and helps protect the pump from overheating.
6. Noise Reduction: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps generally operate at lower noise levels compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The oil acts as a noise-damping medium, reducing the noise generated by the moving parts and the interaction of gases within the pump. This makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as laboratory environments or noise-sensitive industrial settings.
7. Versatility: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are versatile and can handle a wide range of gases and vapors. They can effectively handle both condensable and non-condensable gases, making them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and research laboratories.
8. Cost-Effective: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are often considered cost-effective options for many applications. They generally have a lower initial cost compared to some other types of high-vacuum pumps. Additionally, the maintenance and operating costs are relatively lower, making them an economical choice for industries that require reliable vacuum performance.
9. Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are relatively simple in design and easy to maintain. Routine maintenance typically involves monitoring oil levels, changing the oil periodically, and inspecting and replacing worn-out parts as necessary. The simplicity of maintenance procedures contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
10. Compatibility with Other Equipment: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are compatible with various process equipment and systems. They can be easily integrated into existing setups or used in conjunction with other vacuum-related equipment, such as vacuum chambers, distillation systems, or industrial process equipment.
These advantages make oil-sealed vacuum pumps a popular choice in many industries where reliable, high-performance vacuum systems are required. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and consult with experts to determine the most suitable type of vacuum pump for a particular use case.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Soil and Groundwater Remediation?
Vacuum pumps are indeed widely used for soil and groundwater remediation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Soil and groundwater remediation refers to the process of removing contaminants from the soil and groundwater to restore environmental quality and protect human health. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various remediation techniques by facilitating the extraction and treatment of contaminated media. Some of the common applications of vacuum pumps in soil and groundwater remediation include:
1. Soil Vapor Extraction (SVE): Soil vapor extraction is a widely used remediation technique for volatile contaminants present in the subsurface. It involves the extraction of vapors from the soil by applying a vacuum to the subsurface through wells or trenches. Vacuum pumps create a pressure gradient that induces the movement of vapors towards the extraction points. The extracted vapors are then treated to remove or destroy the contaminants. Vacuum pumps play a vital role in SVE by maintaining the necessary negative pressure to enhance the volatilization and extraction of contaminants from the soil.
2. Dual-Phase Extraction (DPE): Dual-phase extraction is a remediation method used for the simultaneous extraction of both liquids (such as groundwater) and vapors (such as volatile organic compounds) from the subsurface. Vacuum pumps are utilized to create a vacuum in extraction wells or points, drawing out both the liquid and vapor phases. The extracted groundwater and vapors are then separated and treated accordingly. Vacuum pumps are essential in DPE systems for efficient and controlled extraction of both liquid and vapor-phase contaminants.
3. Groundwater Pumping and Treatment: Vacuum pumps are also employed in groundwater remediation through the process of pumping and treatment. They are used to extract contaminated groundwater from wells or recovery trenches. By creating a vacuum or negative pressure, vacuum pumps facilitate the flow of groundwater towards the extraction points. The extracted groundwater is then treated to remove or neutralize the contaminants before being discharged or re-injected into the ground. Vacuum pumps play a critical role in maintaining the required flow rates and hydraulic gradients for effective groundwater extraction and treatment.
4. Air Sparging: Air sparging is a remediation technique used to treat groundwater and soil contaminated with volatile organic compounds (VOCs). It involves the injection of air or oxygen into the subsurface to enhance the volatilization of contaminants. Vacuum pumps are utilized in air sparging systems to create a vacuum or negative pressure zone in wells or points surrounding the contaminated area. This induces the movement of air and oxygen through the soil, facilitating the release and volatilization of VOCs. Vacuum pumps are essential in air sparging by maintaining the necessary negative pressure gradient for effective contaminant removal.
5. Vacuum-Enhanced Recovery: Vacuum-enhanced recovery, also known as vacuum-enhanced extraction, is a remediation technique used to recover non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) or dense non-aqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs) from the subsurface. Vacuum pumps are employed to create a vacuum or negative pressure gradient in recovery wells or trenches. This encourages the movement and extraction of NAPLs or DNAPLs towards the recovery points. Vacuum pumps facilitate the efficient recovery of these dense contaminants, which may not be easily recoverable using traditional pumping methods.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, liquid ring pumps, or air-cooled pumps, may be used in soil and groundwater remediation depending on the specific requirements of the remediation technique and the nature of the contaminants.
In summary, vacuum pumps play a vital role in various soil and groundwater remediation techniques, including soil vapor extraction, dual-phase extraction, groundwater pumping and treatment, air sparging, and vacuum-enhanced recovery. By creating and maintaining the necessary pressure differentials, vacuum pumps enable the efficient extraction, treatment, and removal of contaminants, contributing to the restoration of soil and groundwater quality.

What Is a Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment within a closed system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A vacuum pump operates on the principle of removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber, reducing the pressure inside the chamber to create a vacuum. The pump accomplishes this through various mechanisms and techniques, depending on the specific type of vacuum pump. Here are the basic steps involved in the operation of a vacuum pump:
1. Sealed Chamber:
The vacuum pump is connected to a sealed chamber or system from which air or gas molecules need to be evacuated. The chamber can be a container, a pipeline, or any other enclosed space.
2. Inlet and Outlet:
The vacuum pump has an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is connected to the sealed chamber, while the outlet may be vented to the atmosphere or connected to a collection system to capture or release the evacuated gas.
3. Mechanical Action:
The vacuum pump creates a mechanical action that removes gas molecules from the chamber. Different types of vacuum pumps use various mechanisms for this purpose:
– Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps physically trap gas molecules and remove them from the chamber. Examples include rotary vane pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
– Momentum Transfer Pumps: These pumps use high-speed jets or rotating blades to transfer momentum to gas molecules, pushing them out of the chamber. Examples include turbomolecular pumps and diffusion pumps.
– Entrapment Pumps: These pumps capture gas molecules by adsorbing or condensing them on surfaces or in materials within the pump. Cryogenic pumps and ion pumps are examples of entrainment pumps.
4. Gas Evacuation:
As the vacuum pump operates, it creates a pressure differential between the chamber and the pump. This pressure differential causes gas molecules to move from the chamber to the pump’s inlet.
5. Exhaust or Collection:
Once the gas molecules are removed from the chamber, they are either exhausted into the atmosphere or collected and processed further, depending on the specific application.
6. Pressure Control:
Vacuum pumps often incorporate pressure control mechanisms to maintain the desired level of vacuum within the chamber. These mechanisms can include valves, regulators, or feedback systems that adjust the pump’s operation to achieve the desired pressure range.
7. Monitoring and Safety:
Vacuum pump systems may include sensors, gauges, or indicators to monitor the pressure levels, temperature, or other parameters. Safety features such as pressure relief valves or interlocks may also be included to protect the system and operators from overpressure or other hazardous conditions.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps have varying levels of vacuum they can achieve and are suitable for different pressure ranges and applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed, and the specific application’s requirements.
In summary, a vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. The pump accomplishes this through mechanical actions, such as positive displacement, momentum transfer, or entrapment. By creating a pressure differential, the pump evacuates gas from the chamber, and the gas is either exhausted or collected. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, research, and scientific applications.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
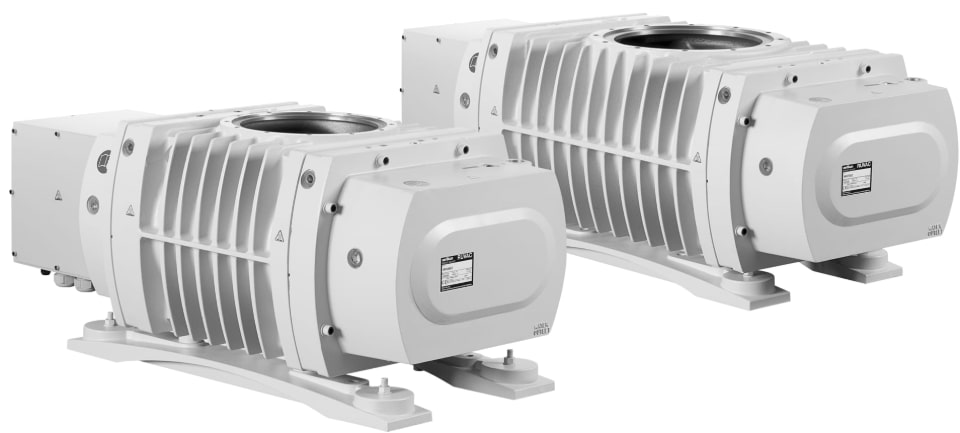
China high quality Roots Vacuum Pumps for Metallurgical, Petrochemical, Papermaking, Food, and Electronic Industries vacuum pump electric
Product Description
Product Description
Roots pump is a kind of vacuum pump without internal compression. It is a vacuum pump that realizes air extraction by moving gas under the pushing action of synchronous and reverse rotation of a pair of “8” shaped rotors in the pump cavity. Generally, the pumping rate is large and the power of the motor is small, so the front pump is required to pre pump. After the front pump reaches the specified vacuum degree, start the roots vacuum pump to improve the pumping speed and vacuum degree. Its structure and working principle are similar to roots blower. During operation, its suction is connected with the evacuated container or the main pump of vacuum system. There is no contact between rotors of Roots vacuum pump and between rotors and pump casing.
Our Advantages
The running parts in the pump have no friction, no lubrication, and there is no oil in the pump cavity, so a clean vacuum can be obtained.
2 leaf involute cycloid profile, high-precision machining to ensure smooth and quiet operation.
the gas in the pump chamber flows vertically, which is conducive to the discharge of dust and condensate in the pumped gas.
. The high-strength rotor with complete symmetry and precise dynamic balance operates stably and reliably.
high precision gear, imported bearing, low vibration and noise.
the new omni-directional three-dimensional water-cooling jacket design can effectively cool the pump body and greatly prolong the service life of the pump.
the overflow surface can be plated with shackles, Hastelloy and PTFE, which can adapt to corrosive environments with different strengths.
it is convenient to form roots vacuum unit with liquid ring vacuum pump, rotary vane vacuum pump and dry vacuum pump.
Typical Use
——Oil and gas recovery. ——Biological medicine ——Food Processing —— Single crystal furnace
——Vacuum forming ——Vacuum flame refining ——Electronic photovoltaic. ——Semiconductor synthesis
Product Parameters
| Type | Pumping Speed L/S | Maximum allowable differential pressure (Pa) | Pump Speed(RPM) | Inlet Diameter(mm) | Outlet Diameter(mm) | Motor Power(kw) |
| ZJB-70 | 70 | 8000 | 2850 | 80 | 50 | 1.5 |
| ZJB-150 | 150 | 6000 | 2850 | 100 | 80 | 3 |
| ZJB-300 | 300 | 5000 | 2900 | 150 | 100 | 4 |
| ZJB-600 | 600 | 4000 | 2900 | 200 | 150 | 5.5Z7.5 |
| ZJ-1200 | 1200 | 3000 | 2900 | 250 | 200 | 11/15 |
| ZJ-2500 | 2500 | 2600 | 2900 | 300 | 250 | 22 |
| ZJ-3750 | 3750 | 2600 | 1450 | 350 | 350 | 30 |
| ZJ-5000 | 5000 | 2600 | 1450 | 400 | 400 | 45 |
Detailed Photos
Vacuum pump is used in the field of chemical and pharmaceutical factory
General Manager Speech
Deeply cultivate the vacuum technology, and research,develop and manufacture the vacuum equipment to provide the best solution in the vacuum field and make the vacuum application easier.
Company Profile
ZheJiang Kaien Vacuum Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise integrating R & D, production and operation of vacuum equipment. The company has strong technical force, excellent equipment and considerate after-sales service. The product manufacturing process is managed in strict accordance with IS09001 quality system. It mainly produces and sells screw vacuum pump, roots pump, claw vacuum pump, runoff vacuum pump, scroll pump, water ring vacuum pump, vacuum unit and other vacuum systems.
New plant plHangZhou
The company’s products have been for a number of food, medicine, refrigeration, drying plants and a number of transformer related equipment manufacturers for vacuum equipment. The products are widely used in vacuum drying and dehydration, kerosene vapor phase drying, vacuum impregnation, vacuum metallurgy, vacuum coating, vacuum evaporation, vacuum concentration, oil and gas recovery, etc.
High precision machining equipment
The company cooperates with colleges and universities to research and develop core technologies, and owns dozens of independent intellectual property patents. Adhering to the basic tenet of quality, reputation and service, the company takes leading-edge technology of vacuum pump as its own responsibility, and wholeheartedly serves customers of vacuum equipment application in various industries with rigorous working attitude and professional working style.
Product quality wins consumer cooperationIn shipment ISO 9001
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Lifetime Paid Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | One Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
| Structure: | Screw |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Significance of Roots Vacuum Pumps in the Aerospace Sector?
Roots vacuum pumps play a significant role in various applications within the aerospace sector. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Space Simulation Chambers:
– Vacuum Simulation: Roots vacuum pumps are utilized in space simulation chambers to create and maintain vacuum conditions similar to the space environment. These chambers are used to test and simulate the performance of aerospace components and systems under low-pressure conditions, including the effects of vacuum on materials, electronics, and mechanical systems.
– Thermal Vacuum Testing: Roots pumps are crucial in thermal vacuum testing, where aerospace components and systems are subjected to extreme temperature and vacuum conditions. The pumps help evacuate the test chamber and maintain the required vacuum level, enabling accurate thermal testing and evaluation of aerospace equipment’s performance and functionality in space-like conditions.
2. Propellant Handling and Storage:
– Rocket Engine Testing: Roots vacuum pumps are employed in rocket engine testing facilities for propellant handling and storage. They assist in creating a vacuum environment during the propellant loading and purging processes, ensuring the removal of air or contaminants from the propellant tanks and lines. This helps maintain the propellant’s quality and prevents potential issues, such as cavitation or gas bubble formation, that could affect engine performance.
– Fuel Systems: Roots pumps are used in aerospace fuel systems to evacuate and degas the fuel tanks, ensuring the removal of air or gas bubbles that may compromise fuel delivery and engine operation. These pumps contribute to the overall efficiency, reliability, and safety of fuel systems in aerospace vehicles.
3. Environmental Control Systems (ECS):
– Cabin Pressure Control: Roots vacuum pumps are utilized in the environmental control systems of aircraft and spacecraft to help control cabin pressure. By creating a vacuum or adjusting the air circulation, these pumps assist in maintaining the desired cabin pressure levels, ensuring passenger comfort, and providing a safe and controlled environment during flight.
4. Avionics and Electronics:
– Electronic Component Testing: Roots vacuum pumps are employed in the testing and validation of avionics and electronic components used in aerospace applications. These pumps assist in creating a controlled vacuum environment during testing, allowing engineers to evaluate the performance, reliability, and durability of electronic systems under low-pressure conditions.
– Vacuum Encapsulation: In certain aerospace applications, electronic components or circuits may require vacuum encapsulation for protection against harsh environmental conditions, including high altitude, temperature variations, or moisture. Roots vacuum pumps are utilized to create the necessary vacuum environment for the encapsulation process, ensuring the integrity and longevity of sensitive electronics.
5. Space Propulsion Systems:
– Ion Thrusters and Electric Propulsion: Roots vacuum pumps are integral components of ion thrusters and electric propulsion systems used in spacecraft. These pumps aid in the creation and maintenance of the high vacuum conditions required for the operation of these advanced propulsion technologies. They contribute to the efficient exhaust gas removal, ensuring optimal thrust generation and fuel efficiency.
6. Satellite Manufacturing and Testing:
– Satellite Chamber Evacuation: Roots vacuum pumps are utilized in satellite manufacturing and testing facilities for the evacuation of satellite chambers. These pumps help create the required vacuum conditions during satellite assembly, testing, and payload integration, ensuring the cleanliness, functionality, and performance of satellite systems and instruments.
In summary, Roots vacuum pumps have significant significance in the aerospace sector. They are utilized in space simulation chambers, propellant handling and storage, environmental control systems, avionics and electronics testing, space propulsion systems, and satellite manufacturing and testing. By creating and maintaining vacuum conditions, Roots pumps contribute to the performance, reliability, and safety of aerospace components, systems, and vehicles. They play a vital role in supporting space exploration, satellite communication, and the advancement of aerospace technologies.
How Do Roots Vacuum Pumps Differ from Other Types of Vacuum Pumps?
Roots vacuum pumps, also known as Roots blowers or rotary lobe pumps, have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of vacuum pumps. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between Roots vacuum pumps and other common types of vacuum pumps:
1. Operating Principle: Roots vacuum pumps operate based on the principle of positive displacement. They use synchronized rotating lobes to trap and compress gas, resulting in the creation of a pressure differential that generates vacuum. Other types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, liquid ring pumps, and diffusion pumps, operate on different principles, such as rotor rotation, liquid sealing, or molecular diffusion.
2. Pumping Mechanism: Roots vacuum pumps are non-contacting pumps, meaning there is no physical contact between the lobes or between the lobes and the housing. This eliminates the need for lubrication within the pump and reduces the risk of contamination or oil vapor backstreaming into the vacuum system. In contrast, many other types of vacuum pumps rely on a sealing mechanism that involves physical contact between moving parts, requiring lubrication to maintain proper operation.
3. Pumping Speed: Roots vacuum pumps are known for their high pumping speed, which refers to the rate at which they can remove gas from a vacuum system. They excel at handling large volumes of gas efficiently. This makes Roots vacuum pumps suitable for applications that require rapid evacuation or continuous extraction of gases. Other types of vacuum pumps may have different pumping speeds depending on their design and intended applications.
4. Vacuum Level: While Roots vacuum pumps are efficient at generating rough vacuum levels, typically in the range of 10 to 1,000 mbar, they are not capable of achieving high vacuum levels on their own. They are often used in conjunction with other vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps or diffusion pumps, in hybrid or combination pumping systems to achieve higher vacuum levels. In contrast, other types of vacuum pumps, such as turbomolecular pumps or cryogenic pumps, are designed specifically for achieving and maintaining high vacuum levels.
5. Gas Handling: Roots vacuum pumps have a large gas handling capacity and can handle a wide range of gases, including clean air, corrosive gases, and vapors. Their robust construction and ability to handle gas with particulates or liquids make them suitable for applications in various industries. Other types of vacuum pumps may have limitations in terms of the types of gases they can handle or may require additional equipment or treatments to handle specific gases.
6. Applications: Roots vacuum pumps find applications in a wide range of industrial processes, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, environmental technology, semiconductor manufacturing, packaging, and research laboratories. Other types of vacuum pumps, such as turbomolecular pumps, cryogenic pumps, or scroll pumps, may be more commonly used in specific industries or applications where their unique operating principles or capabilities are advantageous.
It’s important to note that the selection of a vacuum pump depends on various factors, including the desired vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed requirements, application-specific considerations, and budget constraints. Different types of vacuum pumps offer distinct advantages and are chosen based on the specific requirements of the application.
In summary, Roots vacuum pumps differ from other types of vacuum pumps in terms of their operating principle, pumping mechanism, pumping speed, vacuum level capabilities, gas handling capacity, and applications. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the most suitable vacuum pump for a particular industrial process or application.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China high quality Vacuum Distillation Roots Pump Being in a Larger Working Range vacuum pump electric
Product Description
| Model | Suction capacity (L/S) |
Limit vacuum (≤Pa) |
Speed (rpm) |
Motor Power (kw) |
Inlet Dia. (mm) |
Outlet Dia. (mm) |
Weight (Kg) |
Recommended backing pump model |
| ZJ-70 | 70 | 6×10-2 | 2780 | 1.5 | 80 | 50 | 87 | 2X-8 |
| ZJB-70 | 5×10-2 | 100 | ||||||
| ZJ-150A | 150 | 6×10-2 | 2900 | 3 | 100 | 100 | 198 | 2X-15 |
| ZJB-150 | 5×10-2 | 215 | ||||||
| ZJ-300 | 300 | 6×10-2 | 1450 | 4 | 150 | 150 | 490 | 2X-30A |
| ZJB-300 | 5×10-2 | 480 | ||||||
| ZJ-600 | 600 | 6×10-2 | 2900 | 5.5 | 150 | 150 | 490 | 2X-70A |
| ZJB-600 | 5×10-2 | 503 | ||||||
| ZJ-1200A | 1200 | 6×10-2 | 1450 | 11 | 300 | 300 | 1550 | 2X-70A (2sets) |
| ZJB-1200 | 5×10-2 | 250 | 250 | 1580 |
JZB Roots vacuum pump
1. Construction features and working principle of the pump:
Model ZJ Mechanical Booster Pump, also known as a Roots pump, is a volumetric pump.
It employs a pair of rotors, identical and in 8-figure with certain clearance between them
in the pump housing, rotating at the same speed in opposite directions to perform
function of suction and discharge of gas. The 2 rotors are supported by rolling bearings
in the end covers of the pump, rotating at high speed and are kept at a
fixed relative position by a pair of timing gears. The end clearance between rotors and
end covers are fixed by adjustable metal shims between the bearing housings and the
end cover at the fixed end, which ensures one-direction expansion of the rotor when
temperature rises during its operation.
Four sets of inner seals (also known as piston ring) in the 2 end covers prevent lube oil
entering into the pump housing. The shaft seal at the front-end cover, also called as
framework oil seal or shaft seal, prevents leakage of air into the pump housing.
In order to reduce temperature of the pump, all models of pumps (expect the two
smallest models) are equipped with a gearbox cooler and front-end cover cooler.
Power is transmitted through a coupling or V-belt from the motor to the driving shaft of
the pump and then through synchronizing gears to the driven shaft
Product’s Application
Product Display
Company Power
FAQ
1.Q:Are you a manufacturer or trading company?
A: We are a professional vacuum pump manufacturer with over 32 year experience. We have 2 factories now which cover more than 33333 square meters,we have rich experience in CHINAMFG liquid industry , Welcome to visit our factory at your time.
2.Q:Do you have minimum order quantity request?
A: for spare parts we have no MOQ,but for whole set equipment of course 1 set is the minimum.
3.Q:Do you have certificates?
A: Yes, we have CE, ISO,SGS.etc. certificates.
5.Q:How to pay?
A:T/T and Alibaba Payment is acceptable.
6.Q:How to pack the products?
A: We use standard export package. If you have special package requirements, we will pack as you required, but the fees will be paid by customers.
7.Q: What about your delivery time?
A: It depends on your pump quantity. Generally 15 days after we receive the prepayment. We will confirm you again when we start to produce.
8.Q:How to install after the equipment arriving destination?
A: We will sent the operating instruction with goods to you.Please strictly follow the instructions for installation
9.Q: How long does your product quality warranty last?
A: 12 months for all our products against any non-artificial quality problem since the product leave our factory.
10.Q: What will you do with quality complaint?
A: We have a complete set of microcomputer controlled testing system(All products are subject to tested before delivery. No product that failed performance test leaves our factory.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Warranty: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
| Structure: | Singel Stage |
| Exhauster Method: | Roots Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Low Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Mainsuction Pump |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
Can Roots Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Vacuum Impregnation in Manufacturing?
Yes, Roots vacuum pumps can be used for vacuum impregnation in manufacturing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Vacuum Impregnation in Manufacturing: Vacuum impregnation is a process used in manufacturing to fill porous materials or components with a liquid or resin. It is commonly employed to enhance the properties of materials by improving their strength, sealing capability, or resistance to chemicals or corrosion. The process involves placing the porous material in a vacuum chamber and removing the air or gas trapped within its pores. Once a vacuum is established, a liquid or resin is introduced, and the vacuum is released, allowing the material to absorb the impregnating substance.
2. Role of Roots Vacuum Pumps: Roots vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the vacuum impregnation process by creating and maintaining the required vacuum conditions. Here’s how they contribute:
– Evacuation: Roots pumps are used to evacuate the impregnation chamber, removing the air and gas from within the pores of the porous material. By creating a vacuum, the trapped gases are extracted, creating a void space for the impregnating substance to penetrate.
– Pressure Control: Roots pumps help control the pressure within the impregnation chamber during different stages of the process. They can rapidly achieve and maintain the desired vacuum level, ensuring proper impregnation of the material and preventing the formation of air bubbles or voids.
– Gas Removal: Roots pumps effectively remove gases released from the impregnating substance during the impregnation process. As the liquid or resin fills the pores of the porous material, gases may be released due to the reaction or outgassing. The vacuum pump evacuates these gases, preventing their accumulation and ensuring complete impregnation.
3. Advantages of Roots Vacuum Pumps for Vacuum Impregnation:
– High Pumping Speed: Roots vacuum pumps have a high pumping speed, enabling rapid evacuation of the impregnation chamber. This reduces the overall impregnation cycle time, increasing manufacturing throughput and efficiency.
– Large Volume Handling: Roots pumps are capable of handling large volumes of gas, allowing them to evacuate chambers of different sizes effectively. This is advantageous when impregnating large or complex-shaped components that require a significant amount of impregnating substance.
– Continuous Operation: Roots pumps can operate continuously, maintaining the vacuum conditions required for impregnation throughout the process. This ensures consistent impregnation results and reduces the risk of incomplete impregnation or material defects.
– Compatibility with Impregnating Substances: Roots vacuum pumps are compatible with a wide range of impregnating substances, including resins, oils, solvents, and other liquids. They can handle different chemical compositions and provide a clean and efficient environment for the impregnation process.
4. Considerations for Vacuum Impregnation:
– Material Compatibility: It is essential to consider the compatibility of the porous material with the impregnating substance and the impregnation process itself. Some materials may require pre-treatment or surface preparation before impregnation. The choice of impregnating substance should also align with the material’s properties and intended application.
– Process Parameters: Vacuum impregnation involves controlling various process parameters, such as vacuum level, impregnation time, pressure release, and curing conditions. These parameters may vary depending on the material, impregnating substance, and desired impregnation results. Proper process optimization and control are crucial for achieving consistent and reliable impregnation outcomes.
– System Design: The design of the vacuum impregnation system should consider factors such as chamber size, gas flow rates, vacuum pump capacity, and pressure control mechanisms. Proper system design ensures efficient operation, reliable vacuum conditions, and effective impregnation of the porous material.
In summary, Roots vacuum pumps are well-suited for vacuum impregnation in manufacturing. Their high pumping speed, large volume handling capability, continuous operation, and compatibility with impregnating substances make them effective in creating and maintaining the required vacuum conditions for successful impregnation. By considering material compatibility, process parameters, and system design, Roots vacuum pumps contribute to the efficient and reliable impregnation of porous materials in various manufacturing applications.

What Are the Primary Applications of Roots Vacuum Pumps?
Roots vacuum pumps, also known as Roots blowers or rotary lobe pumps, are utilized in a variety of industrial applications where efficient and reliable vacuum generation is required. Here’s a detailed explanation of the primary applications of Roots vacuum pumps:
1. Chemical Processing: Roots vacuum pumps find extensive use in the chemical processing industry. They are employed for processes such as vacuum distillation, solvent recovery, drying, and degassing. Their high pumping speed and ability to handle corrosive gases make them suitable for handling various chemical vapors and byproducts.
2. Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, Roots vacuum pumps are utilized for applications such as vacuum drying, tablet coating, freeze drying, and vacuum packaging. Their oil-free operation ensures a clean and contaminant-free vacuum environment, which is crucial for pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
3. Food Processing: Roots vacuum pumps play a significant role in the food processing industry. They are employed for vacuum packaging, vacuum cooling, and vacuum drying of food products. The oil-free operation of Roots vacuum pumps ensures food safety and eliminates the risk of contamination.
4. Environmental Technology: Roots vacuum pumps are utilized in environmental technology applications, including wastewater treatment, biogas processing, and air pollution control. They are employed to extract gases, control emissions, and facilitate the treatment and purification of air and water.
5. Semiconductor Manufacturing: In the semiconductor industry, Roots vacuum pumps are used for processes such as ion implantation, physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and etching. Their high pumping speed and oil-free operation are crucial for maintaining clean vacuum conditions required in semiconductor fabrication.
6. Packaging and Printing: Roots vacuum pumps are employed in packaging and printing applications. They are used for vacuum packaging of products, vacuum forming of packaging materials, and in printing presses for paper handling and ink transfer.
7. Automotive Industry: Roots vacuum pumps find application in the automotive industry for processes such as brake system vacuum assist, crankcase ventilation, and emissions control systems. They help create vacuum conditions required for the operation of various automotive systems.
8. Research and Laboratory: Roots vacuum pumps are utilized in research laboratories and scientific facilities for a wide range of applications. They are used in vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, vacuum filtration, electron microscopy, surface analysis, and other laboratory processes that require controlled vacuum environments.
9. Energy Industry: In the energy sector, Roots vacuum pumps are used for applications such as steam turbine condenser air extraction, transformer drying, and vacuum impregnation of electrical components. They help maintain proper vacuum conditions for efficient and reliable operation of energy systems.
These are some of the primary applications where Roots vacuum pumps are commonly used. Their high pumping speed, large gas handling capacity, oil-free operation, reliability, and versatility make them suitable for a wide range of industrial processes that require efficient and reliable vacuum generation.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Best Sales Customized High Air Flow Centrifugal Vacuum Drying Pump vacuum pump belt
Product Description
High Air Flow Centrifugal Vacuum Drying Pump Specifications
| Model | Design | Power | Air flow | Pressure | Vacuum | Weight | |
| KW | m3/h | mbar | mbar | Kgs | |||
| TKS-70 | Single | 2.2-7.5 | 120-1200 | 241 | 224 | 66-93 | |
Model: TKS-70 Brand: CHINAMFG
Frequency: 50/60Hz Motor: IE2 / IE3
Power: 2.2-7.5kw Voltage: 220V / 380V
Air flow: 120-1200m3/h Pressure: -224 / 241mbar
Packages: Packed in cartons Dimension: 750*650*650mm
Installation ways: Vertical and Horizontal Outlet: 360 around
High Air Flow Centrifugal Vacuum Drying Pump Advantages
★ IE2 and IE3 Motor with High class protection
★ Energy Saving
★ Easy to install
★ High Speed and High Air flow
★ Competitive Price with Good Quality
★ Durable and Long time warrenty
High Air Flow Centrifugal Vacuum Drying Pump Applications
A. Ultrasonic Washing & Cleaning & Drying Equipment
B. Fridge board drying
C. Dust-Free Plant
D. Auto part Drying
E. Plastic sheet Drying
F. Electroplating parts Drying
G. Plating Drying and Cleaning System
H. PCBA Cleaning and Drying Equipment
I. Material Handling and Conveying
J. Water Treatment
K. Tank Aeration & Aquaculture & Shrimp (Fish) Farm
L. Vacuum Filling Equipment & Bottling drying system
M. Spa Pool & Swimming Pool Equipment & Jacuzzi Spas
N. Air Coating & Spraying System
O. Biogas Transportation & Biogas Power Generation
P. Sand Blasting Machine
Etc.
SCB Vacuum Company service
A. Professional design and die-casting blowers make sure the stable capacity
B. Engineer Teams help you choosing the best suitable models
C. OEM service available
D. Full products range: ring blowers, belt-driven blowers, Atex blowers, IP55 etc
E. 1 year warrenty, 24hours service support
F. Super quality with Competitive Price
G. Delivery time is 1week after payment
H. Certificates: CCC, CE, TUV
High Air Flow Centrifugal Vacuum Drying Pump Introduction
CHINAMFG Vacuum are a company which develop blower for some years. Our main products is belt-driven pump, vacuum blower, vacuum blower, regenerative blower, ring blower, side channel blower and all parts. The full range models will support you much well in the market.
Belt-driven pump are using Die-casting technique, to make sure provide all blowers with stable the capacity and peformance.
The terms we appreciate is FOB, CFR, CIF and EXW etc.
Welcome contact us for more technical information and competitive price!
| SCB | Fanny |
| SCB Vacuum Tech Limited | |
| Add: C402, Kaisong Industrial Park, Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Xihu (West Lake) Dis., HangZhou, ZheJiang Province, China | |
| Web: vacuumblower |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
| Samples: |
US$ 1618/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What Are the Advantages of Using Oil-Sealed Vacuum Pumps?
Oil-sealed vacuum pumps offer several advantages in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. High Vacuum Performance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are known for their ability to achieve high levels of vacuum. They can create and maintain deep vacuum levels, making them suitable for applications that require a low-pressure environment. The use of oil as a sealing and lubricating medium helps in achieving efficient vacuum performance.
2. Wide Operating Range: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps have a wide operating range, allowing them to handle a broad spectrum of vacuum levels. They can operate effectively in both low-pressure and high-vacuum conditions, making them versatile for different applications across various industries.
3. Efficient and Reliable Operation: These pumps are known for their reliability and consistent performance. The oil-sealed design provides effective sealing, preventing air leakage and maintaining a stable vacuum level. They are designed to operate continuously for extended periods without significant performance degradation, making them suitable for continuous industrial processes.
4. Contamination Handling: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are effective in handling certain types of contaminants that may be present in the process gases or air being evacuated. The oil acts as a barrier, trapping and absorbing certain particulates, moisture, and chemical vapors, preventing them from reaching the pump mechanism. This helps protect the pump internals from potential damage and contributes to the longevity of the pump.
5. Thermal Stability: The presence of oil in these pumps helps in dissipating heat generated during operation, contributing to their thermal stability. The oil absorbs and carries away heat, preventing excessive temperature rise within the pump. This thermal stability allows for consistent performance even during prolonged operation and helps protect the pump from overheating.
6. Noise Reduction: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps generally operate at lower noise levels compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The oil acts as a noise-damping medium, reducing the noise generated by the moving parts and the interaction of gases within the pump. This makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as laboratory environments or noise-sensitive industrial settings.
7. Versatility: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are versatile and can handle a wide range of gases and vapors. They can effectively handle both condensable and non-condensable gases, making them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and research laboratories.
8. Cost-Effective: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are often considered cost-effective options for many applications. They generally have a lower initial cost compared to some other types of high-vacuum pumps. Additionally, the maintenance and operating costs are relatively lower, making them an economical choice for industries that require reliable vacuum performance.
9. Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are relatively simple in design and easy to maintain. Routine maintenance typically involves monitoring oil levels, changing the oil periodically, and inspecting and replacing worn-out parts as necessary. The simplicity of maintenance procedures contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
10. Compatibility with Other Equipment: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are compatible with various process equipment and systems. They can be easily integrated into existing setups or used in conjunction with other vacuum-related equipment, such as vacuum chambers, distillation systems, or industrial process equipment.
These advantages make oil-sealed vacuum pumps a popular choice in many industries where reliable, high-performance vacuum systems are required. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and consult with experts to determine the most suitable type of vacuum pump for a particular use case.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Soil and Groundwater Remediation?
Vacuum pumps are indeed widely used for soil and groundwater remediation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Soil and groundwater remediation refers to the process of removing contaminants from the soil and groundwater to restore environmental quality and protect human health. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various remediation techniques by facilitating the extraction and treatment of contaminated media. Some of the common applications of vacuum pumps in soil and groundwater remediation include:
1. Soil Vapor Extraction (SVE): Soil vapor extraction is a widely used remediation technique for volatile contaminants present in the subsurface. It involves the extraction of vapors from the soil by applying a vacuum to the subsurface through wells or trenches. Vacuum pumps create a pressure gradient that induces the movement of vapors towards the extraction points. The extracted vapors are then treated to remove or destroy the contaminants. Vacuum pumps play a vital role in SVE by maintaining the necessary negative pressure to enhance the volatilization and extraction of contaminants from the soil.
2. Dual-Phase Extraction (DPE): Dual-phase extraction is a remediation method used for the simultaneous extraction of both liquids (such as groundwater) and vapors (such as volatile organic compounds) from the subsurface. Vacuum pumps are utilized to create a vacuum in extraction wells or points, drawing out both the liquid and vapor phases. The extracted groundwater and vapors are then separated and treated accordingly. Vacuum pumps are essential in DPE systems for efficient and controlled extraction of both liquid and vapor-phase contaminants.
3. Groundwater Pumping and Treatment: Vacuum pumps are also employed in groundwater remediation through the process of pumping and treatment. They are used to extract contaminated groundwater from wells or recovery trenches. By creating a vacuum or negative pressure, vacuum pumps facilitate the flow of groundwater towards the extraction points. The extracted groundwater is then treated to remove or neutralize the contaminants before being discharged or re-injected into the ground. Vacuum pumps play a critical role in maintaining the required flow rates and hydraulic gradients for effective groundwater extraction and treatment.
4. Air Sparging: Air sparging is a remediation technique used to treat groundwater and soil contaminated with volatile organic compounds (VOCs). It involves the injection of air or oxygen into the subsurface to enhance the volatilization of contaminants. Vacuum pumps are utilized in air sparging systems to create a vacuum or negative pressure zone in wells or points surrounding the contaminated area. This induces the movement of air and oxygen through the soil, facilitating the release and volatilization of VOCs. Vacuum pumps are essential in air sparging by maintaining the necessary negative pressure gradient for effective contaminant removal.
5. Vacuum-Enhanced Recovery: Vacuum-enhanced recovery, also known as vacuum-enhanced extraction, is a remediation technique used to recover non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) or dense non-aqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs) from the subsurface. Vacuum pumps are employed to create a vacuum or negative pressure gradient in recovery wells or trenches. This encourages the movement and extraction of NAPLs or DNAPLs towards the recovery points. Vacuum pumps facilitate the efficient recovery of these dense contaminants, which may not be easily recoverable using traditional pumping methods.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, liquid ring pumps, or air-cooled pumps, may be used in soil and groundwater remediation depending on the specific requirements of the remediation technique and the nature of the contaminants.
In summary, vacuum pumps play a vital role in various soil and groundwater remediation techniques, including soil vapor extraction, dual-phase extraction, groundwater pumping and treatment, air sparging, and vacuum-enhanced recovery. By creating and maintaining the necessary pressure differentials, vacuum pumps enable the efficient extraction, treatment, and removal of contaminants, contributing to the restoration of soil and groundwater quality.

What Is a Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment within a closed system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A vacuum pump operates on the principle of removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber, reducing the pressure inside the chamber to create a vacuum. The pump accomplishes this through various mechanisms and techniques, depending on the specific type of vacuum pump. Here are the basic steps involved in the operation of a vacuum pump:
1. Sealed Chamber:
The vacuum pump is connected to a sealed chamber or system from which air or gas molecules need to be evacuated. The chamber can be a container, a pipeline, or any other enclosed space.
2. Inlet and Outlet:
The vacuum pump has an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is connected to the sealed chamber, while the outlet may be vented to the atmosphere or connected to a collection system to capture or release the evacuated gas.
3. Mechanical Action:
The vacuum pump creates a mechanical action that removes gas molecules from the chamber. Different types of vacuum pumps use various mechanisms for this purpose:
– Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps physically trap gas molecules and remove them from the chamber. Examples include rotary vane pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
– Momentum Transfer Pumps: These pumps use high-speed jets or rotating blades to transfer momentum to gas molecules, pushing them out of the chamber. Examples include turbomolecular pumps and diffusion pumps.
– Entrapment Pumps: These pumps capture gas molecules by adsorbing or condensing them on surfaces or in materials within the pump. Cryogenic pumps and ion pumps are examples of entrainment pumps.
4. Gas Evacuation:
As the vacuum pump operates, it creates a pressure differential between the chamber and the pump. This pressure differential causes gas molecules to move from the chamber to the pump’s inlet.
5. Exhaust or Collection:
Once the gas molecules are removed from the chamber, they are either exhausted into the atmosphere or collected and processed further, depending on the specific application.
6. Pressure Control:
Vacuum pumps often incorporate pressure control mechanisms to maintain the desired level of vacuum within the chamber. These mechanisms can include valves, regulators, or feedback systems that adjust the pump’s operation to achieve the desired pressure range.
7. Monitoring and Safety:
Vacuum pump systems may include sensors, gauges, or indicators to monitor the pressure levels, temperature, or other parameters. Safety features such as pressure relief valves or interlocks may also be included to protect the system and operators from overpressure or other hazardous conditions.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps have varying levels of vacuum they can achieve and are suitable for different pressure ranges and applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed, and the specific application’s requirements.
In summary, a vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. The pump accomplishes this through mechanical actions, such as positive displacement, momentum transfer, or entrapment. By creating a pressure differential, the pump evacuates gas from the chamber, and the gas is either exhausted or collected. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, research, and scientific applications.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China high quality China Factory Wholesale Customize OEM ODM Service Slurry Pump, Vacuum Pump, Submersible Pump, Pump Spare Parts vacuum pump connector
Product Description
OEM Pump Support Housing, Pump Motor Body, Cast Iron Casting, Quality Casting Manufacturer
With our automatic sand molding line, it great improve the iron casting quality ,save the manufacturing cost, and help the lead time.
We can supply very competitive price with good quality, fast lead time, efficient quotation, feel free to email us the RFQ for CHINAMFG parts.
We have 2 factory shops for sand casting products,cast from the material of cast iron, ductile iron casting, aluminum, brass. We have both towering CHINAMFG for big melting volume and intermediate frequency furnaces for less melting volume. The annual output capability is more than 1000 tons. Our mainly sand casting parts is: for the diesel oil vehicles of engine body and impeller, various water pump body and housing, for the food industry machine, such as tomato mill machine parts of body and Spiral, meat mincer machine parts of body,Spiral and ring. We also can cast the big body for grinding or lathe machine.
We can supply official Material Chemical report, Tenstile testing report.
FAQ
1.What do you need to provide a quote?
Please kindly send us the drawing of your product. Details below should be included,
A.Materials B. Surface Finish C. Tolerance D. Quantity
(Please be noted that these are essential for our quoting. We couldn’t quote the specific
price without any of them.).
2.When can I get the price?
Our professional sales team will feedback your RFQ within 12hours, and give you the Quotation within 48hours max. if the drawing and specification is all in details.
3.How can I get the sample to check your quality?
After price confirmation, you can require for samples to check our product’s quality. If you just need a blank sample to check the manufacturing quality, we will provide you sample after the sample order confirmed.
4.What’s the lead time for Mould and samples ?
For normal project, we can complete Mould and supply the 1st article sample within 30 to 40days.
For urgently project, we can complete the Mould and Sample within 20days max.
5.What’s the payment terms for Order ?
For Mould/tooling and sample : 50% deposit pay by Order, rest 50% pay after sample approval.
For production Order for new Customers : we request 30% down payment, rest 70% pay by copy of Original B/L copy. For long lasting regular customer, we can give better payment terms, such as 100% pay after delivery or by B/L copy.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Clay Dry Sand |
|---|---|
| Casting Method: | Aluminum Sand Casting |
| Sand Core Type: | Resin Sand Core |
| Application: | Machinery Parts |
| Machining: | CNC Machining |
| Material: | Aluminum A356 |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Vacuum Furnaces?
Yes, vacuum pumps can be used for vacuum furnaces. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum furnaces are specialized heating systems used in various industries for heat treatment processes that require controlled environments with low or no atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in creating and maintaining the vacuum conditions necessary for the operation of vacuum furnaces.
Here are some key points regarding the use of vacuum pumps in vacuum furnaces:
1. Vacuum Creation: Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the furnace chamber, creating a low-pressure or near-vacuum environment. This is essential for the heat treatment processes carried out in the furnace, as it helps eliminate oxygen and other reactive gases, preventing oxidation or unwanted chemical reactions with the heated materials.
2. Pressure Control: Vacuum pumps provide the means to control and maintain the desired pressure levels within the furnace chamber during the heat treatment process. Precise pressure control is necessary to achieve the desired metallurgical and material property changes during processes such as annealing, brazing, sintering, and hardening.
3. Contamination Prevention: By removing gases and impurities from the furnace chamber, vacuum pumps help prevent contamination of the heated materials. This is particularly important in applications where cleanliness and purity of the processed materials are critical, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
4. Rapid Cooling: Some vacuum furnace systems incorporate rapid cooling capabilities, known as quenching. Vacuum pumps assist in facilitating the rapid cooling process by removing the heat generated during quenching, ensuring efficient cooling and minimizing distortion or other unwanted effects on the treated materials.
5. Process Flexibility: Vacuum pumps provide flexibility in the type of heat treatment processes that can be performed in vacuum furnaces. Different heat treatment techniques, such as vacuum annealing, vacuum brazing, or vacuum carburizing, require specific pressure levels and atmospheric conditions that can be achieved and maintained with the use of vacuum pumps.
6. Vacuum Pump Types: Different types of vacuum pumps can be used in vacuum furnaces, depending on the specific requirements of the heat treatment process. Commonly used vacuum pump technologies include oil-sealed rotary vane pumps, dry screw pumps, diffusion pumps, and cryogenic pumps. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as required vacuum level, pumping speed, reliability, and compatibility with the process gases.
7. Maintenance and Monitoring: Proper maintenance and monitoring of vacuum pumps are essential to ensure their optimal performance and reliability. Regular inspections, lubrication, and replacement of consumables (such as oil or filters) are necessary to maintain the efficiency and longevity of the vacuum pump system.
8. Safety Considerations: Operating vacuum furnaces with vacuum pumps requires adherence to safety protocols. This includes proper handling of potentially hazardous gases or chemicals used in the heat treatment processes, as well as following safety guidelines for operating and maintaining the vacuum pump system.
Overall, vacuum pumps are integral components of vacuum furnaces, enabling the creation and maintenance of the required vacuum conditions for precise and controlled heat treatment processes. They contribute to the quality, consistency, and efficiency of the heat treatment operations performed in vacuum furnaces across a wide range of industries.

What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to support a range of critical operations. Some of the key roles of vacuum pumps in pharmaceutical manufacturing include:
1. Drying and Evaporation: Vacuum pumps are employed in drying and evaporation processes within the pharmaceutical industry. They facilitate the removal of moisture or solvents from pharmaceutical products or intermediates. Vacuum drying chambers or evaporators utilize vacuum pumps to create low-pressure conditions, which lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate at lower temperatures. By applying vacuum, moisture or solvents can be efficiently removed from substances such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), granules, powders, or coatings, ensuring the desired product quality and stability.
2. Filtration and Filtrate Recovery: Vacuum pumps are used in filtration processes for the separation of solid-liquid mixtures. Vacuum filtration systems typically employ a filter medium, such as filter paper or membranes, to retain solids while allowing the liquid portion to pass through. By applying vacuum to the filtration apparatus, the liquid is drawn through the filter medium, leaving behind the solids. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient filtration, speeding up the process and improving product quality. Additionally, vacuum pumps can aid in filtrate recovery by collecting and transferring the filtrate for further processing or reuse.
3. Distillation and Purification: Vacuum pumps are essential in distillation and purification processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Distillation involves the separation of liquid mixtures based on their different boiling points. By creating a vacuum environment, vacuum pumps lower the boiling points of the components, allowing them to vaporize and separate more easily. This enables efficient separation and purification of pharmaceutical compounds, including the removal of impurities or the isolation of specific components. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various distillation setups, such as rotary evaporators or thin film evaporators, to achieve precise control over the distillation conditions.
4. Freeze Drying (Lyophilization): Vacuum pumps are integral to the freeze drying process, also known as lyophilization. Lyophilization is a dehydration technique that involves the removal of water or solvents from pharmaceutical products while preserving their structure and integrity. Vacuum pumps create a low-pressure environment in freeze drying chambers, allowing the frozen product to undergo sublimation. During sublimation, the frozen water or solvent directly transitions from the solid phase to the vapor phase, bypassing the liquid phase. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient and controlled sublimation, leading to the production of stable, shelf-stable pharmaceutical products with extended shelf life.
5. Tablet and Capsule Manufacturing: Vacuum pumps are utilized in tablet and capsule manufacturing processes. They are involved in the creation of vacuum within tablet presses or capsule filling machines. By applying vacuum, the air is removed from the die cavity or capsule cavity, allowing for the precise filling of powders or granules. Vacuum pumps contribute to the production of uniform and well-formed tablets or capsules by ensuring accurate dosing and minimizing air entrapment, which can affect the final product quality.
6. Sterilization and Decontamination: Vacuum pumps are employed in sterilization and decontamination processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Autoclaves and sterilizers utilize vacuum pumps to create a vacuum environment before introducing steam or chemical sterilants. By removing air or gases from the chamber, vacuum pumps assist in achieving effective sterilization or decontamination by enhancing the penetration and distribution of sterilants. Vacuum pumps also aid in the removal of sterilants and residues after the sterilization process is complete.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry screw pumps, or liquid ring pumps, may be utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing depending on the specific requirements of the process and the compatibility with pharmaceutical products.
In summary, vacuum pumps play a vital role in various stages of pharmaceutical manufacturing, including drying and evaporation, filtration and filtrate recovery, distillation and purification, freeze drying (lyophilization), tablet and capsule manufacturing, as well as sterilization and decontamination. By enabling efficient and controlled processes, vacuum pumps contribute to the production of high-quality pharmaceutical products, ensuring the desired characteristics, stability, and safety.

What Is the Purpose of a Vacuum Pump in an HVAC System?
In an HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system, a vacuum pump serves a crucial purpose. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The purpose of a vacuum pump in an HVAC system is to remove air and moisture from the refrigerant lines and the system itself. HVAC systems, particularly those that rely on refrigeration, operate under specific pressure and temperature conditions to facilitate the transfer of heat. To ensure optimal performance and efficiency, it is essential to evacuate any non-condensable gases, air, and moisture from the system.
Here are the key reasons why a vacuum pump is used in an HVAC system:
1. Removing Moisture: Moisture can be present within an HVAC system due to various factors, such as system installation, leaks, or improper maintenance. When moisture combines with the refrigerant, it can cause issues like ice formation, reduced system efficiency, and potential damage to system components. A vacuum pump helps remove moisture by creating a low-pressure environment, which causes the moisture to boil and turn into vapor, effectively evacuating it from the system.
2. Eliminating Air and Non-Condensable Gases: Air and non-condensable gases, such as nitrogen or oxygen, can enter an HVAC system during installation, repair, or through leaks. These gases can hinder the refrigeration process, affect heat transfer, and decrease system performance. By using a vacuum pump, technicians can evacuate the air and non-condensable gases, ensuring that the system operates with the designed refrigerant and pressure levels.
3. Preparing for Refrigerant Charging: Prior to charging the HVAC system with refrigerant, it is crucial to create a vacuum to remove any contaminants and ensure the system is clean and ready for optimal refrigerant circulation. By evacuating the system with a vacuum pump, technicians ensure that the refrigerant enters a clean and controlled environment, reducing the risk of system malfunctions and improving overall efficiency.
4. Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are also used in HVAC systems for leak detection purposes. After evacuating the system, technicians can monitor the pressure to check if it holds steady. A significant drop in pressure indicates the presence of leaks, enabling technicians to identify and repair them before charging the system with refrigerant.
In summary, a vacuum pump plays a vital role in an HVAC system by removing moisture, eliminating air and non-condensable gases, preparing the system for refrigerant charging, and aiding in leak detection. These functions help ensure optimal system performance, energy efficiency, and longevity, while also reducing the risk of system malfunctions and damage.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China manufacturer 06D145100d Turbo Engine Brake Vacuum Pump for Audi Tt Quattro VW vacuum pump design
Product Description
| 1. Price : | EXW Price |
| 2.Shipping Way: | By Sea, DHL, UPS, FEDEX or as customers’ requirements |
| 3.Payment Terms: | Via T/T ,L/C ,Paypal ,Westerm Union,Moneygram. |
| 4.Delivery Time: | Within 30 days after deposit or as customers’ requirement |
| 5.Packaging:Packaging: |
1.Carton Box, 4.We can perform according to customer’s requirements |
Ideer Established in 2571, which is a professional manufacturer and exporter that is concerned with the design, development and production of auto parts. We are located in HangZhou, with convenient transportation access. All of our productscomply with international quality standards and are greatly appreciated in a variety of different markets throughout the world.
Covering an area of 10000 square meters, we now have over 100 employees, an annual sales figure that exceeds USD 300,000 and are currently exporting 80% of our production worldwide. Our well-equipped facilities and excellent quality control throughout all stages of production enables us to guarantee total customer satisfaction.
Besides, we have received ISO9001 and CE.As a result of our high quality products and outstanding customer service, we have gained a global sales network CZPT South America.
If you are interested in any of our products or would like to discuss a customorder, please feel free to contact us. We are looking CZPT to forming successful business relationships with new clients around the world in the near future.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 24 Hours |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1years |
| Type: | Brake System |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Types of vacuum pumps
A vacuum pump is a device that draws gas molecules from a sealed volume and maintains a partial vacuum. Its job is to create a vacuum in a volume, usually one of several. There are several types of vacuum pumps, such as root pumps, diaphragm pumps, rotary piston pumps, and self-priming centrifugal pumps.
The diaphragm pump is a dry positive displacement vacuum pump
Diaphragm pumps are a versatile type of vacuum pump. They can be installed in a variety of scenarios including container emptying, positive suction, and simultaneous fluid mixing. Their performance depends on the stiffness and durability of the diaphragm, which in turn depends on the material.
They have good performance when running in dry mode. Diaphragm pumps work very similarly to the human heart, which is why they are often used to create artificial hearts. In addition, the diaphragm pump is self-priming and has high efficiency. They are also capable of handling the most viscous liquids and are used in almost all industries.
However, this type of pump has several disadvantages. One of them is that they are difficult to restart after a power outage. Another disadvantage is that they can generate a lot of heat. Fortunately, this heat is carried away by airflow. However, this heat builds up in the multistage pump. If this happens, the diaphragm or motor may be damaged. Diaphragm pumps operating in two or more stages should be fitted with solenoid valves to maintain vacuum stability.
Diaphragm pumps are a good choice for drying processes where hygiene is important. These pumps have check valves and rubber or Teflon diaphragms. Diaphragm pumps are also ideal for high viscosity applications where shear sensitivity is important.
Roots pumps are dry method centrifugal pumps
Roots pumps use a vane rotor pump with two counter-rotating vanes that move in opposite directions to move the gas. They are often the first choice for high-throughput process applications. Depending on the size and number of blades, they can withstand up to 10 Torr.
Centrifugal pumps have several advantages, including the ability to handle corrosive fluids and high temperatures. However, when choosing a pump, it is essential to choose a reputable manufacturer. These companies will be able to advise you on the best pump design for your needs and provide excellent after-sales support. Roots pumps can be used in a wide range of industrial applications including chemical, food, and biotechnology.
The Roots pump is a dry centrifugal pump whose geometry enables it to achieve high compression ratios. The screw rotors are synchronized by a set of timing gears that allow gas to pass in both directions and create a compressed state in the chamber. The pre-compressed gas is discharged through a pressure connection and cooled with water. Some pumps are also able to accept additional cooling gas, but this should be done with caution.
The size of the impeller plays an important role in determining the pump head. The impeller diameter determines how high the pump can lift the liquid. Impeller speed also affects the head. Since the head is proportional to the specific gravity of the liquid, the available suction pressure will be proportional to the density of the liquid. The density of water is about 1.2 kg/m3, and the suction pressure of the centrifugal pump is not enough to lift the water.
The rotary vane pump is a self-priming centrifugal pump
A rotary vane pump is a centrifugal pump with a circular pump head and a cycloid cam that supports the rotor. The rotor is close to the cam wall, and two side plates seal the rotor. Vanes in vane pumps are installed in these cavities, and the rotor rotates at high speed, pushing fluid in and out of the pump. The pump offers several advantages, including a reversible design and the ability to handle a wide variety of clean fluids.
Agknx Pumps manufactures a wide range of vane pumps that combine high performance, low cost, and easy maintenance. These pumps handle medium to high viscosity liquids up to 500 degrees Fahrenheit and 200,000 SSU.
The suction side of the rotary vane pump has a discharge port, and the valve prevents the backflow of the discharge air. When the maximum pressure is reached, the outlet valve closes to prevent the backflow of exhaust gas. The mechanical separation step separates the oil from the gas in the pump circuit and returns the remaining oil particles to the sump. The float valve then reintroduces these oil particles into the oil circuit of the pump. The gas produced is almost oil-free and can be blown out of a pipe or hose.
Rotary vane pumps are self-priming positive displacement pumps commonly used in hydraulic, aeration, and vacuum systems. Unlike gear pumps, rotary vane pumps can maintain high-pressure levels while using relatively low suction pressures. The pump is also very effective when pumping viscous or high-viscosity liquids. 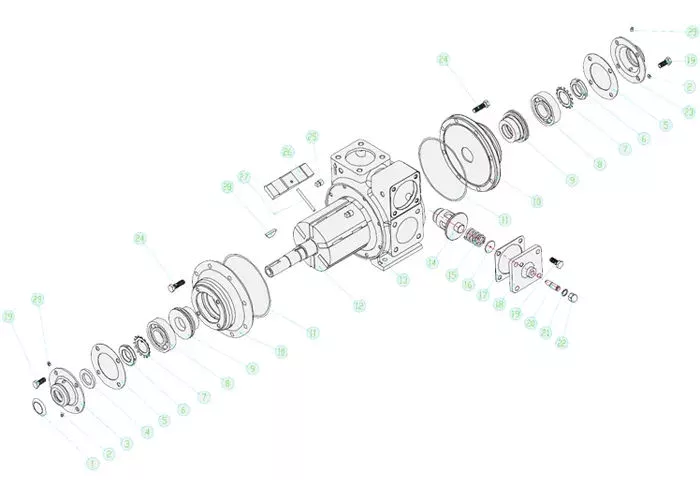
Rotary piston pumps are dry method positive displacement pumps
Rotary piston pumps are dry positive displacement pumps designed to deliver high-viscosity fluids. They are capable of pumping a variety of liquids and can run dry without damaging the liquid. Rotary piston pumps are available in a variety of designs. Some are single shafts, some are two shafts and four bearings.
Positive displacement pumps operate slower than centrifugal pumps. This feature makes the positive displacement pump more sensitive to wear. Piston and plunger reciprocating pumps are particularly prone to wear. For more demanding applications, progressive cavity, diaphragm or lobe pumps may be a better choice.
Positive displacement pumps are typically used to pump high-viscosity fluids. This is because the pump relies on a mechanical seal between the rotating elements and the pump casing. As a result, when fluids have low viscosity, their performance is limited. Additionally, low viscosity fluids can cause valve slippage.
These pumps have a piston/plunger arrangement using stainless steel rotors. Piston/piston pumps have two cavities on the suction side. The fluid then flows from one chamber to the other through a helical motion. This results in very low shear and pulsation rates. The pump is usually installed in a cylindrical housing.
Rotary vane pump corrosion resistance
Rotary vane vacuum pumps are designed for use in a variety of industries. They feature plasma-treated corrosion-resistant parts and anti-suck-back valves to help reduce the number of corrosive vapors entering the pump. These pumps are commonly used in freeze dryers, vacuum ovens, and degassing processes. The high flow rates they provide in their working vacuum allow them to speed up processes and reduce the time it takes to run them. Plus, they have energy-efficient motors and silent volume. <br/While rotary vane vacuum pumps are relatively corrosion resistant, they should not be used for aggressive chemicals. For these chemicals, the most suitable pump is the chemical mixing pump, which combines two types of pumps to improve corrosion resistance. If the application requires a more powerful pump, a progressive cavity pump (eg VACUU*PURE 10C) is suitable.
Oil seals used in rotary vane pumps are important to pump performance. The oil seal prevents corrosion of the aluminum parts of the rotary vane pump and prolongs the service life. Most rotary vane vacuum pumps have a standard set of components, although each component may have different oil seals.
Rotary vane vacuum pumps are the most common type of positive displacement pump. They provide quiet operation and long service life. They are also reliable and inexpensive and can be used in a variety of applications. 
Roots pumps are primarily used as a vacuum booster
Root vacuum pumps are mainly used as vacuum boosters in industrial applications. They need a thorough understanding of operating principles and proper maintenance to function properly. This course is an introduction to Roots vacuum pumps, covering topics such as pump principles, multi-stage pumps, temperature effects, gas cooling, and maintenance.
Roots pumps have many advantages, including compact and quiet operation. They do not generate particles and have a long service life. They also don’t require oil and have a small footprint. However, Roots pumps have several disadvantages, including relatively high maintenance costs and low pumping speeds near atmospheric pressure.
Root vacuum pumps are often used with rotary vane vacuum pumps. They work on the same principle, the air enters a conveying unit formed by two rolling pistons in the housing. The piston heads are separated from each other, and the air passes through the unit without being reduced until it is discharged. When the air in the next unit reaches a higher absolute pressure, it is expelled from the last unit.
Roots pumps can be classified as sheathed or sealed. Roots pumps with sealed motors are suitable for pumping toxic gases. They have less clearance between the stator and motor rotor and have a sealed tank.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Good quality Mbc0500 Roots Vacuum Pumps for Industrial Leak Detection Systems vacuum pump design
Product Description
MBC0500 Mechanical Boosters / Roots Vacuum Pumps
Our MB-C, MB-E, and MB-Y mechanical vacuum booster are oil free vacuum pumps that are running together with the backing pumps for all rough and high-vacuum applications where large pumping speeds are needed. Our vacuum boosters operate totally contact-free and with no sealing fluids such as oil or water exiting in the vacuum chamber. MB-Y vacuum boosters are equipped with bypass valve.
Economical
Due to the large number of available models, the pumping speed and ultimate vacuum can be customized exactly according to specific processes. The high pumping efficiency ensures further increase in the economy of operating costs.
Safe operation
Tried-and-tested engineering technology together with a robust design enables safe operation to happen. The MB-Y series’ integrated bypass valve allows the vacuum boosters to operate at a high pressure level.
| Technical data | 50HZ | MBC0500 |
| Pumping Speed | m3/h | 500 |
| Ultimate pressure | mbar(abs) | 1×10-3 |
| Diameter | “ | VG63/ISO100 |
| Voltage | V | 320-440 |
| Nominal motor rating | Kw | 2.2 |
| Current | A | 3.9/4.0 |
| Nominal speed | Min-1 | 900/1120 |
| Sound | dB(A) | 68 |
| Oil (max) | L | 4.6/5.0 |
| Weight | Kg | 79.5 |
Application Ranges
- Metallurgy
- Simulation chambers
- Packaging industry
- Freeze/vacuum-drying
- Thin-film technology
- Electron beam welding
- Chemistry and process technology
- Industrial leak detection systems
- Steel degassing
- Load-lock chambers
- vacuum impregnation
- vacuum degass
- vacuum pre-discharging
- gas exhausting
- Glass and wear protection coating
- Decorative coating
- Vacuum furnaces
- Space simulation chambers
- for the processes in vacuum distillation, vacuum concentration and vacuum drying in chemical industry, medicine, food and beverage, light industry and textile industry
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Roots Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Kinetic Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Maintain the Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Dry |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Roots Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Vacuum Impregnation in Manufacturing?
Yes, Roots vacuum pumps can be used for vacuum impregnation in manufacturing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Vacuum Impregnation in Manufacturing: Vacuum impregnation is a process used in manufacturing to fill porous materials or components with a liquid or resin. It is commonly employed to enhance the properties of materials by improving their strength, sealing capability, or resistance to chemicals or corrosion. The process involves placing the porous material in a vacuum chamber and removing the air or gas trapped within its pores. Once a vacuum is established, a liquid or resin is introduced, and the vacuum is released, allowing the material to absorb the impregnating substance.
2. Role of Roots Vacuum Pumps: Roots vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the vacuum impregnation process by creating and maintaining the required vacuum conditions. Here’s how they contribute:
– Evacuation: Roots pumps are used to evacuate the impregnation chamber, removing the air and gas from within the pores of the porous material. By creating a vacuum, the trapped gases are extracted, creating a void space for the impregnating substance to penetrate.
– Pressure Control: Roots pumps help control the pressure within the impregnation chamber during different stages of the process. They can rapidly achieve and maintain the desired vacuum level, ensuring proper impregnation of the material and preventing the formation of air bubbles or voids.
– Gas Removal: Roots pumps effectively remove gases released from the impregnating substance during the impregnation process. As the liquid or resin fills the pores of the porous material, gases may be released due to the reaction or outgassing. The vacuum pump evacuates these gases, preventing their accumulation and ensuring complete impregnation.
3. Advantages of Roots Vacuum Pumps for Vacuum Impregnation:
– High Pumping Speed: Roots vacuum pumps have a high pumping speed, enabling rapid evacuation of the impregnation chamber. This reduces the overall impregnation cycle time, increasing manufacturing throughput and efficiency.
– Large Volume Handling: Roots pumps are capable of handling large volumes of gas, allowing them to evacuate chambers of different sizes effectively. This is advantageous when impregnating large or complex-shaped components that require a significant amount of impregnating substance.
– Continuous Operation: Roots pumps can operate continuously, maintaining the vacuum conditions required for impregnation throughout the process. This ensures consistent impregnation results and reduces the risk of incomplete impregnation or material defects.
– Compatibility with Impregnating Substances: Roots vacuum pumps are compatible with a wide range of impregnating substances, including resins, oils, solvents, and other liquids. They can handle different chemical compositions and provide a clean and efficient environment for the impregnation process.
4. Considerations for Vacuum Impregnation:
– Material Compatibility: It is essential to consider the compatibility of the porous material with the impregnating substance and the impregnation process itself. Some materials may require pre-treatment or surface preparation before impregnation. The choice of impregnating substance should also align with the material’s properties and intended application.
– Process Parameters: Vacuum impregnation involves controlling various process parameters, such as vacuum level, impregnation time, pressure release, and curing conditions. These parameters may vary depending on the material, impregnating substance, and desired impregnation results. Proper process optimization and control are crucial for achieving consistent and reliable impregnation outcomes.
– System Design: The design of the vacuum impregnation system should consider factors such as chamber size, gas flow rates, vacuum pump capacity, and pressure control mechanisms. Proper system design ensures efficient operation, reliable vacuum conditions, and effective impregnation of the porous material.
In summary, Roots vacuum pumps are well-suited for vacuum impregnation in manufacturing. Their high pumping speed, large volume handling capability, continuous operation, and compatibility with impregnating substances make them effective in creating and maintaining the required vacuum conditions for successful impregnation. By considering material compatibility, process parameters, and system design, Roots vacuum pumps contribute to the efficient and reliable impregnation of porous materials in various manufacturing applications.

Can Roots Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Vacuum Distillation?
Yes, Roots vacuum pumps can be used for vacuum distillation in certain applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum distillation is a process used to separate and purify components of a liquid mixture by exploiting the difference in boiling points under reduced pressure. By operating at lower pressures, the boiling points of the components are decreased, allowing for more selective evaporation and separation. Vacuum distillation is commonly employed in industries such as petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and chemical manufacturing.
Roots vacuum pumps can play a role in vacuum distillation processes by assisting in the creation and maintenance of the required vacuum conditions. Although Roots vacuum pumps alone may not achieve the high vacuum levels necessary for certain applications, they are often used in combination with other vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps or oil-sealed pumps, to create a hybrid pumping system.
In a typical setup, Roots vacuum pumps are utilized as the primary roughing pump in the distillation system. Their high pumping speed allows for efficient removal of large volumes of gas, reducing the pressure in the system and enabling the effective operation of subsequent stages. The Roots pump works by trapping and compressing the gas, creating a pressure differential that facilitates the evacuation of the system.
While Roots vacuum pumps are effective in generating rough vacuum levels, they may not be capable of achieving the very high vacuum levels often required for precise separation in vacuum distillation. Therefore, they are commonly used in conjunction with other vacuum pumps, such as oil-sealed pumps or molecular pumps, that are better suited for achieving and maintaining high vacuum levels.
It’s important to note that the selection and configuration of the vacuum pumps for vacuum distillation depend on various factors, including the desired vacuum level, the characteristics of the liquid mixture being distilled, and the specific requirements of the distillation process. The vacuum system needs to be carefully designed to ensure optimal performance and efficient separation.
In summary, while Roots vacuum pumps alone may not be sufficient for achieving the high vacuum levels required for vacuum distillation, they are commonly employed as part of a hybrid pumping system in conjunction with other vacuum pumps. Their high pumping speed and capability to handle large gas volumes make them valuable for creating the initial vacuum conditions in the distillation process.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Hot selling Customized 0.75kw Power Electric Roots Vacuum Air Pump for Industrial Boilers vacuum pump
Product Description
Customized 0.75kw Power Electric Roots Vacuum Air Pump for Industrial Boilers
Product Description
Product Parameters
|
Model |
ZJ-30 |
ZJ-70 |
ZJ-150 |
ZJ-300 |
ZJ-600 |
ZJ-1200 |
ZJ-2500 |
ZJ-5000 |
|
Ultimate total pressure(Pa) |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
|
Motor Power(Kw) |
0.75 |
1.5 |
3 |
4 |
7.5 |
11 |
22 |
45 |
|
Nominal Motor speed(rpm) |
2850 |
2850 |
2870 |
1450 |
2900 |
1400 |
2880 |
1450 |
|
Nominal Motor current(A) |
1.8 |
3.4 |
6.2 |
15.4 |
14.8 |
22.3 |
41 |
84.7 |
|
Pumping size(mm) |
650X315X255 |
770X315X255 |
1060X462X380 |
1330X556X505 |
1410X556X505 |
1710X1070X850 |
1820X1070X850 |
2700X1200X1100 |
|
Weight (with oil filling)kg |
76 |
96 |
200 |
502 |
520 |
1550 |
1620 |
4000 |
|
Type of protection(IP) |
55 |
55 |
55 |
55 |
55 |
55 |
55 |
55 |
Detailed Photos
Roots vacuum pump (abbreviated as Roots pump) is a rotary variable capacity vacuum pump without internal compression. It utilizes 2 8-shaped rotors to rotate in the pump casing to generate suction and exhaust effects. Its principle is similar to that of a Roots blower. Due to its operation in a low pressure range, the gas molecules have a large free range, and the resistance of gas leakage through small slits is high, so it can achieve a high compression ratio and can be used as a booster vacuum pump; But it cannot directly discharge the gas into the atmosphere alone, and needs to be used in series with the front stage vacuum pump. The extracted gas is carried into the atmosphere through the front stage vacuum pump.
Roots pumps are widely used in vacuum degassing, vacuum melting, vacuum treatment of molten steel in the vacuum metallurgy industry, as well as in devices such as space simulation and low-density wind tunnels to extract corrosive gases. It can also be used in production processes such as distillation, evaporation, and drying in industries such as chemical, food, pharmaceutical, and motor manufacturing.
The ZJ series Roots vacuum pump is a rotary variable capacity vacuum pump that requires a front stage pump to be used. It has a large pumping speed in a wide pressure range in China and is not sensitive to dust and water vapor in the extracted gas. It is widely used in industries such as metallurgy, chemical industry, food, and electronic coating.
Company Profile
HangZhou Sifang Vacuum Equipment Co., Ltd. specializes in the production of vacuum furnaces, vacuum pumps, steel drums and other products.”Sifang” is the registered trademark of the company’s products.
our company is 1 professional vacuum equipment manufacturer in HangZhou, China. We specialize in vacuum pumps, furnaces, systems and components for diverse applications. We produce rotary vane vacuum pumps, water ring vacuum pumps, reciprocating vacuum pumps, roots vacuum pump units, vacuum heat treatment furnaces, vacuum aluminum brazing furnaces, high temperature brazing fur- naces, vacuum sintering furnaces, monocrystalline silicon furnaces and other products. All these vacuum equipment are widely used in aviation, aerospace, military, railway, automobile, machinery, mold, electronics, metallurgy, scientific research and other fields.
We have professional engineer support, high efficiency sales team and competitive price superiority, and attract customers from all over the world, we export to over 40 countries, including Europe, Poland, Serbia, Turkey, Russia, USA, Mexico, Brazil, India, Thailand, Middle east and South Africa.
After several years’ development, We have achieved great progress, we are equipped with the AutomaticCNCmachines and multi-func- tion testing machines. Our R&D department provide the strong tech- nical support and enable us to receive some 0 E M, O D M projects. We can produce at least 3000 sets vacuum equipment per year. With our innovative and energy-efficient vacuum equipment that is put to work in a multitude of manufacturing and process applica- tions, we also offer you a comprehensive suite of CHINAMFG ser- vices to complement our products.
FAQ
1.Q: Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are a factory and we have professional team of workers,Designers and inspectors.
2.Q:Do you accept custom?
A:Of course.We have professional teams who make your designs,photos,imagines and OEM orders into real production.
3.Q:What’s your advantages?
A: Quick response to your enquiry,
High quality control,
Reasonable price,
Timely delivery,
Excellent after-sales service,
OEM/ODM are welcome
4.Q:What’s your shipping terms?
A:If you need to ship by air,we can use DHL,UPS,FedEx,TNT or EMS.If you need to ship by sea,we have many good forwarders to work with,they can provide the best price for you.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
| Structure: | Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Vacuum |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Are Roots Vacuum Pumps Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
Roots vacuum pumps play a significant role in various applications within the automotive industry. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Brake System Vacuum Pumps:
– Vacuum Boosters: Roots vacuum pumps are commonly used as vacuum boosters in automotive brake systems. They assist in enhancing the braking performance by providing the necessary vacuum for power brake operation. When the driver applies the brake pedal, the vacuum booster uses the suction power generated by the Roots pump to amplify the force applied to the brake master cylinder, resulting in more effective braking.
– Electric Brake Vacuum Pumps: In modern electric or hybrid vehicles, where traditional engine-driven vacuum sources may not be available, electric brake vacuum pumps are utilized. These pumps, often based on the Roots principle, generate vacuum independently to power the brake booster and ensure reliable braking performance.
2. Emissions Control:
– Evaporative Emission Control: Roots vacuum pumps are employed in evaporative emission control systems to prevent the release of harmful vapors from the fuel system into the atmosphere. These pumps create a vacuum within the system, purging and storing fuel vapors in a canister for subsequent combustion or recycling.
– Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV): PCV systems, which are designed to reduce emissions and maintain the integrity of the engine, also utilize Roots vacuum pumps. These pumps draw crankcase gases and vapors, including oil mist, from the engine’s crankcase into the intake manifold for combustion, improving overall engine efficiency and reducing pollution.
3. Engine Testing and Development:
– Vacuum Leakage Testing: Roots vacuum pumps are utilized for vacuum leakage testing in engine manufacturing and development. By creating a vacuum in the intake manifold or other engine components, these pumps enable the detection of leaks and ensure the integrity of the engine’s air delivery system.
– Air Flow Calibration: During engine testing and calibration, Roots vacuum pumps are used to simulate various operating conditions by controlling the intake air flow. This allows engineers to fine-tune the engine’s performance, optimize fuel-air mixture ratios, and assess the engine’s efficiency and emissions characteristics.
4. HVAC Systems:
– Climate Control: Roots vacuum pumps are employed in automotive HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems to facilitate the flow and distribution of air. These pumps help regulate the operation of HVAC components, such as air blend doors and vacuum actuators, ensuring proper air temperature and direction control inside the vehicle cabin.
5. Fuel System and Turbocharging:
– Fuel Transfer and Evacuation: In automotive fuel systems, Roots vacuum pumps are used for fuel transfer and evacuation. These pumps assist in priming the fuel system, removing air pockets, and ensuring the continuous flow of fuel to the engine, enhancing the overall fuel delivery performance.
– Turbocharger Control: Roots vacuum pumps are sometimes employed in turbocharged engines to control the actuation of variable geometry turbochargers (VGT). These pumps provide the necessary vacuum signals to actuate the VGT mechanism, optimizing turbocharger performance and enhancing engine efficiency.
6. Other Applications:
– Electric Vehicle Battery Systems: In electric vehicles, Roots vacuum pumps are utilized to create a vacuum in battery enclosures, helping to maintain the integrity and safety of the battery system by preventing the ingress of moisture, dust, or contaminants.
– Engine Air Induction: Some automotive engines utilize Roots-type superchargers or twin-screw superchargers, which are essentially positive displacement Roots vacuum pumps operating in reverse. These devices compress and force air into the engine’s intake manifold, resulting in increased engine power and performance.
In summary, Roots vacuum pumps find extensive utilization in the automotive industry. They play a crucial role in brake systems, emissions control, engine testing and development, HVAC systems, fuel systems, turbocharging, electric vehicle battery systems, and engine air induction. By contributing to braking performance, emissions reduction, engine calibration, HVAC functionality, fuel system efficiency, turbocharger control, battery system safety, and engine power enhancement, Roots vacuum pumps contribute significantly to the overall operation and performance of automotive systems and components.
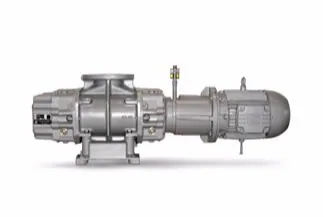
What Is a Roots Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A Roots vacuum pump, also known as a Roots blower or a rotary lobe pump, is a type of positive displacement vacuum pump that is widely used for various industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a Roots vacuum pump is and how it works:
A Roots vacuum pump consists of two synchronized rotors, known as lobes or impellers, that rotate in opposite directions within a housing. The lobes have a unique helical shape with multiple lobes, which allows them to trap and move gas efficiently. The rotors are synchronized with the help of timing gears to maintain precise clearances between the lobes and the housing.
The operation of a Roots vacuum pump can be described in the following steps:
1. Inlet Stage: The process begins with the lobes rotating in opposite directions. As the lobes rotate, the volume between them and the housing gradually increases, creating a larger space at the inlet side of the pump. This expansion of the volume causes the gas to enter the pump through the inlet port. The gas is drawn in due to the pressure difference between the inlet and the pump’s internal chamber.
2. Compression Stage: As the gas enters the pump, it gets trapped in the spaces between the lobes and the housing. As the lobes continue to rotate, the trapped gas gets carried along the rotating lobes. The gas is essentially trapped in the pockets formed by the lobes and the housing. The rotating lobes then compress the gas as they move towards the outlet side of the pump.
3. Outlet Stage: As the lobes approach the outlet side of the pump, the volume between them and the housing decreases, resulting in the compression of the trapped gas. This compression raises the pressure of the gas, causing it to be expelled through the outlet port of the pump. The expelled gas is then discharged into the atmosphere or directed to a downstream process or another vacuum pump, depending on the application.
It’s important to note that a Roots vacuum pump operates as a non-contacting pump, meaning that there is no physical contact between the lobes or between the lobes and the housing. This characteristic eliminates the need for lubrication within the pump and reduces the risk of contamination or oil vapor backstreaming into the vacuum system.
Roots vacuum pumps are known for their high pumping speed and ability to handle large volumes of gas. However, they are not capable of achieving high vacuum levels on their own. To achieve higher vacuum levels, a Roots pump is often used in conjunction with other vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps or diffusion pumps, in a hybrid or combination pumping system.
In summary, a Roots vacuum pump operates based on the principle of positive displacement. It utilizes synchronized rotating lobes to trap and compress gas, allowing it to be discharged at a higher pressure. The non-contacting design of the pump eliminates the need for lubrication and reduces the risk of contamination. Roots vacuum pumps are commonly employed in various industrial applications, especially when high pumping speed and large gas handling capacity are required.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09